Animal models of drug-induced liver injury
- PMID: 31007174
- PMCID: PMC6478394
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.08.037
Animal models of drug-induced liver injury
Abstract
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) presents unique challenges for consumers, clinicians, and regulators. It is the most common cause of acute liver failure in the US. It is also one of the most common reasons for termination of new drugs during pre-clinical testing and withdrawal of new drugs post-marketing. DILI is generally divided into two forms: intrinsic and idiosyncratic. Many of the challenges with DILI are due in large part to poor understanding of the mechanisms of toxicity. Although useful models of intrinsic DILI are available, they are frequently misused. Modeling idiosyncratic DILI presents greater challenges, but promising new models have recently been developed. The purpose of this manuscript is to provide a critical review of the most popular animal models of DILI, and to discuss the future of DILI research.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; Carbon tetrachloride; Idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity; Immune tolerance; Intrinsic hepatotoxicity.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures
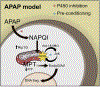
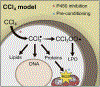
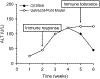
References
-
- Ganger DR, Rule J, Rakela J, Bass N, Reuben A, Stravitz R, Sussman N, Larson AM, James L, Chiu C, Lee WM, Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Acute Liver Failure of Indeterminate Etiology: A Comprehensive Systematic Approach by An Expert Committee to Establish Causality. Am J Gastroenterol 2018; June 27. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0160-2. [Epub ahead of print] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Issa AM, Phillips KA, Van Bebber S, Nidamarthy HG, Lasser KE, Haas JS, Alldredge BK, Wachter RM, Bates DW. Drug withdrawals in the United States: a systematic review of the evidence and analysis of trends. Curr Drug Saf 2007; 2:177–85. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

