Targeting the Blood-Brain Barrier to Prevent Sepsis-Associated Cognitive Impairment
- PMID: 31007531
- PMCID: PMC6456845
- DOI: 10.1177/1179573519840652
Targeting the Blood-Brain Barrier to Prevent Sepsis-Associated Cognitive Impairment
Abstract
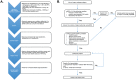
Sepsis is a systemic inflammatory disease resulting from an infection. This disorder affects 750 000 people annually in the United States and has a 62% rehospitalization rate. Septic symptoms range from typical flu-like symptoms (eg, headache, fever) to a multifactorial syndrome known as sepsis-associated encephalopathy (SAE). Patients with SAE exhibit an acute altered mental status and often have higher mortality and morbidity. In addition, many sepsis survivors are also burdened with long-term cognitive impairment. The mechanisms through which sepsis initiates SAE and promotes long-term cognitive impairment in septic survivors are poorly understood. Due to its unique role as an interface between the brain and the periphery, numerous studies support a regulatory role for the blood-brain barrier (BBB) in the progression of acute and chronic brain dysfunction. In this review, we discuss the current body of literature which supports the BBB as a nexus which integrates signals from the brain and the periphery in sepsis. We highlight key insights on the mechanisms that contribute to the BBB's role in sepsis which include neuroinflammation, increased barrier permeability, immune cell infiltration, mitochondrial dysfunction, and a potential barrier role for tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase (TNAP). Finally, we address current drug treatments (eg, antimicrobials and intravenous immunoglobulins) for sepsis and their potential outcomes on brain function. A comprehensive understanding of these mechanisms may enable clinicians to target specific aspects of BBB function as a therapeutic tool to limit long-term cognitive impairment in sepsis survivors.
Keywords: Sepsis; blood-brain barrier; drug delivery; neuroinflammation; sepsis-associated encephalopathy; tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Martin AB, Hartman M, Benson J, Catlin A; National Health Expenditure Accounts Team. National health spending in 2014: faster growth driven by coverage expansion and prescription drug spending. Health Aff (Millwood). 2016;35:150–160. - PubMed
-
- Gofton TE, Young GB. Sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2012;8:557–566. - PubMed
-
- Widmann CN, Heneka MT. Long-term cerebral consequences of sepsis. Lancet Neurol. 2014;13:630–636. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

