Postoperative analgesia with ropivacaine and dexmedetomidine for ultrasound-guided fascia iliaca compartment block after arthroscopic knee surgery
- PMID: 31007654
- PMCID: PMC6448445
- DOI: 10.4103/sja.SJA_533_18
Postoperative analgesia with ropivacaine and dexmedetomidine for ultrasound-guided fascia iliaca compartment block after arthroscopic knee surgery
Abstract
Objective: The objective of this study is to evaluate the postoperative analgesic effect of a combination of ropivacaine and dexmedetomidine for ultrasound-guided fascia iliaca compartment block (FICB) after knee arthroscopy.
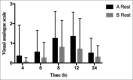
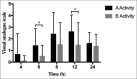
Materials and methods: Forty patients scheduled for knee arthroscopy were randomized to receive either 30 ml of 0.25% ropivacaine alone (Group A, n = 20) or combined with dexmedetomidine 1 μg/kg (Group B, n = 20). Pain intensity was evaluated using the visual analogue scale (VAS), at rest and during activity at 4, 6, 8, 12, and 24 h after surgery. Level of consciousness was evaluated using the Ramsay sedation score. Time to first analgesic request after surgery, the dose of analgesic used in the first 24 h after surgery, variation of heart rate, and adverse reactions were also recorded.
Results: VAS scores at 6 and 12 h after surgery were significantly lower in Group B compared to Group A (P < 0.05). No significant difference was observed in the Ramsay sedation score or time to first analgesic request after surgery (P > 0.05). The total dose of analgesic used in the first 24 h after surgery was higher in Group A than in Group B. The incidence of bradycardia was higher in Group B compared to Group A. No adverse reactions were observed in either group.
Conclusion: FICB with a combination of ropivacaine and dexmedetomidine resulted in significant reduction of VAS scores with lower postoperative analgesic requirement after arthroscopic knee surgery. No adverse reactions or complications were noted except for lower heart rate in Group B patients.
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine; knee arthroscopy; ropivacaine; ultrasound-guided fascia iliaca compartment block.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-guided dexmedetomidine combination with modified high fascia iliaca compartment block for arthroscopic knee surgery: what is the optimal dose of dexmedetomidine?BMC Anesthesiol. 2023 Dec 6;23(1):400. doi: 10.1186/s12871-023-02361-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023. PMID: 38057762 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block with dexmedetomidine and ropivacaine on postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023 Oct 20;85(12):5977-5982. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001427. eCollection 2023 Dec. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2023. PMID: 38098568 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Dexmedetomidine as a Local Anesthetic Adjuvant for Iliac Fascia Compartment Block on Postoperative Delirium in Elderly Patients Undergoing Elective Hip Surgery.Gerontology. 2024;70(5):491-498. doi: 10.1159/000536651. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Gerontology. 2024. PMID: 38479368 Clinical Trial.
-
Analgesic effect of ropivacaine combined with dexmedetomidine in the postoperative period in children undergoing ultrasound-guided single-shot sacral epidural block: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Pediatr. 2023 Mar 29;11:1099699. doi: 10.3389/fped.2023.1099699. eCollection 2023. Front Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37063658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postsurgical analgesic efficacy by the intra-articular administration of ropivacaine with dexmedetomidine versus simple ropivacaine in patients undergoing knee arthroscopy.Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2024 May-Jun;68(3):306-312. doi: 10.1016/j.recot.2022.12.001. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2024. PMID: 36567063 Review. English, Spanish.
Cited by
-
[Impact of post-thoracotomy analgesia with dexmedetomidine and morphine on immunocytes: a randomized clinical trial].Braz J Anesthesiol. 2020 Mar-Apr;70(2):153-158. doi: 10.1016/j.bjan.2019.12.017. Epub 2020 May 13. Braz J Anesthesiol. 2020. PMID: 32505378 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Abdallah FW, Brull R. Facilitatory effects of perineural dexmedetomidine on neuraxial and peripheral nerve block: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110:915–25. - PubMed
-
- Wallace JB, Andrade JA, Christensen JP, Osborne LA, Pellegrini JE. Comparison of fascia iliaca compartment block and 3-in-1 block in adults undergoing knee arthroscopy and meniscal repair. AANA J. 2012;80:S37–44. - PubMed