An overview of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 31007693
- PMCID: PMC6450139
- DOI: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_256_18
An overview of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli (DEC) is a common enteric pathogen that causes a wide spectrum of gastrointestinal infections, particularly in developing countries. This is a systematic review and meta-analysis to determine the prevalence of DEC in various geographical regions in Iran.
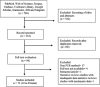
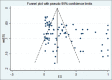
Materials and methods: English (PubMed, Web of Science, Scopus, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar) and Persian (IranMedex, SID, Magiran, and Iran Doc) databases were comprehensively searched from January 1990 to April 2017. Study selection and data extraction were performed by two independent reviewers. After assessing heterogeneity among studies, a random effects model was applied to estimate pooled prevalence. Data analyses were done with the Stata software (version 12.0). This meta-analysis was registered with PROSPERO, number CRD42017070411.
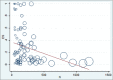
Results: A total of 73 studies with 18068 isolates were eligible for inclusion within the meta-analysis. The results of random effects model showed that the most prevalent DEC pathotypes were enterotoxigenic E. coli (ETEC) (16%; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 11%-23%), enteroaggregative E. coli (11%; 95% CI: 8%-15%), atypical enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) (11%; 95% CI: 8%-14%), Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (9%; 95% CI: 6%-13%), diffuse adherent E. coli (6%; 95% CI: 6%-12%), enteroinvasive E. coli (4%; 95% CI: 2%-6%), and typical EPEC (3%; 95% CI: 1%-5%).
Conclusion: This study showed that DEC infections in the Iranian population have low frequency. Our data suggest that the ETEC pathotype can be regarded as one of the most important etiological agents of diarrhea in this country. However, the prevalence of DEC pathotypes is diverse in different regions of Iran.
Keywords: Diarrhea; Escherichia coli; Iran; meta-analysis; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Oliveira FA, Paludo KS, Arend LN, Farah SM, Pedrosa FO, Souza EM, et al. Virulence characteristics and antimicrobial susceptibility of uropathogenic Escherichia coli strains. Genet Mol Res. 2011;10:4114–25. - PubMed
-
- Kim HJ, Koo M, Jeong AR, Baek SY, Cho JI, Lee SH, et al. Occurrence of pathogenic Escherichia coli in commercially available fresh vegetable products in Korea. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem. 2014;57:367–70.
-
- Banu A, Kabbin JS, Anand M. Extraintestinal infections due to Escherichia coli: An emerging issue. J Clin Diagn Res. 2011;5:486–90.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

