Combined metabolic, phenomic and genomic data to prioritize atrial fibrillation-related metabolites
- PMID: 31007735
- PMCID: PMC6468506
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7443
Combined metabolic, phenomic and genomic data to prioritize atrial fibrillation-related metabolites
Abstract
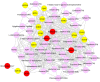
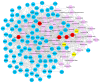
Metabolites in atrial fibrillation (AF) were characterized to further explore the molecular mechanisms of AF by integrating metabolic, phenomic and genomic data. Gene expression data on AF (E-GEOD-79768) were downloaded from the EMBL-EBI database, followed by identification of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) which were used to construct gene-gene network. Then, multi-omics composite networks were constructed. Subsequently, random walk with restart was expanded to a multi-omics composite network to identify and prioritize the metabolites according to the AF-related seed genes deposited in the OMIM database, the whole metabolome as candidates and the phenotype of AF. Using the interaction score among metabolites, we extracted the top 50 metabolites, and identified the top 100 co-expressed genes interacted with the top 50 metabolites. Based on the FDR <0.05, 622 DEGs were extracted. In order to demonstrate the intrinsic mode of this method, we sorted the metabolites of the composite network in descending order based on the interaction scores. The top 5 metabolites were respectively weighed potassium, sodium ion, chitin, benzo[a]pyrene-7,8-dihydrodiol-9,10-oxide, and celebrex (TN). Potassium and sodium ion possessed higher degrees in the subnetwork of the entire composite network and the co-expressed network. Metabolites such as potassium and sodium ion may provide valuable clues for early diagnostic and therapeutic targets for AF.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; metabolite; multi-omics composite network; sinus rhythm.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
