Population pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in pediatric refractory nephrotic syndrome and a summary of other pediatric disease models
- PMID: 31007740
- PMCID: PMC6468928
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7446
Population pharmacokinetics of tacrolimus in pediatric refractory nephrotic syndrome and a summary of other pediatric disease models
Abstract
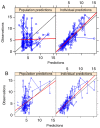
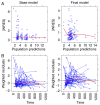
Different tacrolimus (TAC) population pharmacokinetic (PPK) models have been established in various pediatric disease populations. However, a TAC PPK model for pediatric refractory nephrotic syndrome (PRNS) has not been well characterized. The current study aimed to establish a TAC PPK model in Chinese PRNS and provide a summary of previous literature concerning TAC PPK models in different pediatric diseases. A total of 147 TAC conventional therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) data from multiple blood samples obtained from 65 Chinese patients with PRNS were characterized using nonlinear mixed-effects modeling. The impacts of demographic features, biological characteristics and drug combination were evaluated. Model validation was assessed using the bootstrap method. A one-compartment model with first-order absorption and elimination was determined to be the most suitable model for TDM data in PRNS. The absorption rate constant (Ka) was set at 4.48 h-1. The typical values of apparent oral clearance (CL/F) and apparent volume of distribution (V/F) in the final model were 5.46 l/h and 57.1 l, respectively. The inter-individual variability of CL/F and V/F were 22.2 and 0.2%, respectively. The PPK equation for TAC was: CL/F = 5.46 × exponential function (EXP)(0.0323 × age) × EXP(-0.359 × cystatin-C) × EXP(0.148 × daily dose of TAC). No significant effects of covariates on V/F were observed. In conclusion, the current study developed and validated the first TAC PPK model for patients with PRNS. The study also provided a summary of previous literature concerning other TAC PPK models in different pediatric diseases.
Keywords: nonlinear mixed-effects modeling; pediatric refractory nephrotic syndrome; population pharmacokinetics; tacrolimus; therapeutic drug monitoring.
Figures
References
-
- Certikova-Chabova V, Tesar V. Recent insights into the pathogenesis of nephrotic syndrome. Minerva Med. 2013;104:333–347. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
