Prediction of seed gene function in progressive diabetic neuropathy by a network-based inference method
- PMID: 31007748
- PMCID: PMC6468912
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.7441
Prediction of seed gene function in progressive diabetic neuropathy by a network-based inference method
Abstract
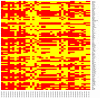
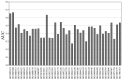
Guilt by association (GBA) algorithm has been widely used to statistically predict gene functions, and network-based approach increases the confidence and veracity of identifying molecular signatures for diseases. This work proposed a network-based GBA method by integrating the GBA algorithm and network, to identify seed gene functions for progressive diabetic neuropathy (PDN). The inference of predicting seed gene functions comprised of three steps: i) Preparing gene lists and sets; ii) constructing a co-expression matrix (CEM) on gene lists by Spearman correlation coefficient (SCC) method and iii) predicting gene functions by GBA algorithm. Ultimately, seed gene functions were selected according to the area under the receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC) index. A total of 79 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) and 40 background gene ontology (GO) terms were regarded as gene lists and sets for the subsequent analyses, respectively. The predicted results obtained from the network-based GBA approach showed that 27.5% of all gene sets had a good classified performance with AUC >0.5. Most significantly, 3 gene sets with AUC >0.6 were denoted as seed gene functions for PDN, including binding, molecular function and regulation of the metabolic process. In summary, we predicted 3 seed gene functions for PDN compared with non-progressors utilizing network-based GBA algorithm. The findings provide insights to reveal pathological and molecular mechanism underlying PDN.
Keywords: co-expression; gene function; guilt by association; network; progressive diabetic neuropathy.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
