Informed Consent in Biomedical Research
- PMID: 31007872
- PMCID: PMC6458444
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2019.03.010
Informed Consent in Biomedical Research
Abstract
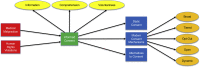
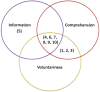
Informed consent is the result of tumultuous events in both the clinical and research arenas over the last 100 years. Throughout this time, the notion of informed consent has shifted tremendously, both due to advances in medicine, as well as the type of data being gathered. As such, informed consent has misaligned with the goals of medical research. It is becoming more and more vital to address this chasm, and begin building new frameworks to link this disconnect. Thus, we address three goals in this paper. First, we discuss the history of informed consent and unify the varying definitions of the term. Second, we evaluate the current research on the topic, classify them into themes, and attend to the problems therein. Lastly, we employ these themes of informed consent research mentioned previously to provide guidance and insight for future research in the arena.
Keywords: Biomedical data; Biomedical research; Informed consent; Medical care; Privacy.
Figures
References
-
- Institutional Review Board Required components of informed consent. https://www.irb.cornell.edu/forms/consent.htm
-
- Rhodes R. In defense of the duty to participate in biomedical research. Am J Bioeth. 2008;8:37–38. - PubMed
-
- Rennie S. Regarding research participation as a moral obligation: who shoulders the burdens and who reaps the benefits? Asian Bioeth Rev. 2010;2:308–321.
-
- Ioannidis J.P. Informed consent, big data, and the oxymoron of research that is not research. Am J Bioeth. 2013;13:40–42. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials