Comparative genomics of 10 new Caenorhabditis species
- PMID: 31007946
- PMCID: PMC6457397
- DOI: 10.1002/evl3.110
Comparative genomics of 10 new Caenorhabditis species
Abstract
The nematode Caenorhabditis elegans has been central to the understanding of metazoan biology. However, C. elegans is but one species among millions and the significance of this important model organism will only be fully revealed if it is placed in a rich evolutionary context. Global sampling efforts have led to the discovery of over 50 putative species from the genus Caenorhabditis, many of which await formal species description. Here, we present species descriptions for 10 new Caenorhabditis species. We also present draft genome sequences for nine of these new species, along with a transcriptome assembly for one. We exploit these whole-genome data to reconstruct the Caenorhabditis phylogeny and use this phylogenetic tree to dissect the evolution of morphology in the genus. We reveal extensive variation in genome size and investigate the molecular processes that underlie this variation. We show unexpected complexity in the evolutionary history of key developmental pathway genes. These new species and the associated genomic resources will be essential in our attempts to understand the evolutionary origins of the C. elegans model.
Keywords: C. elegans; genomics; morphology; phylogenomics; species description.
Figures

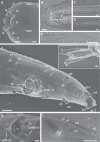
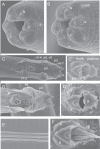

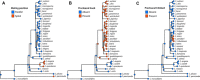
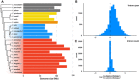

References
-
- Andrássy, I. 1983. A taxonomic review of the suborder Rhabditina (Nematoda: Secernentia). Office de la Recherche Scientifique et Technique Outre‐Mer (ORSTOM), Paris.
-
- Andrews, S. 2010. FastQC: a quality control tool for high throughput sequence data.
-
- Artavanis‐Tsakonas, S. , Rand M. D., and Lake R. J.. 1999. Notch signaling: cell fate control and signal integration in development. Science, 284, 770–776. - PubMed
-
- Barrière, A. , and Félix M.‐A.. 2014. Isolation of C. elegans and related nematodes. WormBook, 2, 1–19. - PubMed

