Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return: A case series with management approach
- PMID: 31008046
- PMCID: PMC6456451
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2019.100833
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return: A case series with management approach
Abstract
Partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (PAPVR) is a rare congenital anomaly that results in a left-to-right shunt. Based on the shunt fraction, PAPVR has a wide spectrum of presentations. If a significant left-to-right shunt is left unrepaired, pulmonary vascular remodeling can occur resulting in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). Furthermore, if the condition is associated with an atrial septal defect (ASD), the patient can develop shunt reversal and Eisenmenger's syndrome in setting of severe PAH. Management plans include close observation, surgical repair, and treatment with pulmonary artery vasodilator therapies. Here, we present multiple cases of PAPVR to highlight the wide spectrum of presentations and the individualized treatment for each case.
Keywords: ASD; CHD; PAH; PAPVR.
Figures

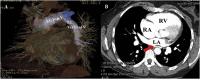
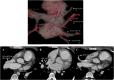


References
-
- Winslow J. Mem. Acad. Roy. Sci. 1739:113.
-
- Latson L.A., Prieto L.R. Congenital and acquired pulmonary vein stenosis. Circulation. 2007;115(1):103–108. - PubMed
-
- Healey J.E., Jr. An anatomic survey of anomalous pulmonary veins: their clinical significance. J. Thorac. Surg. 1952;23:433–444. - PubMed
-
- Ho M.L., Bhalla S., Bierhals A., Gutierrez F. MDCT of partial anomalous pulmonary venous return (PAPVR) in adults. J. Thorac. Imaging. 2009;24:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Alsoufi B., Cai S., Van Arsdell G.S. Outcomes after surgical treatment of children with partial anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2007;84:2020. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

