Bioethanol production from sugarcane leaf waste: Effect of various optimized pretreatments and fermentation conditions on process kinetics
- PMID: 31008065
- PMCID: PMC6453773
- DOI: 10.1016/j.btre.2019.e00329
Bioethanol production from sugarcane leaf waste: Effect of various optimized pretreatments and fermentation conditions on process kinetics
Abstract
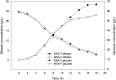
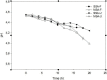
This study examines the kinetics of S. cerevisiae BY4743 growth and bioethanol production from sugarcane leaf waste (SLW), utilizing two different optimized pretreatment regimes; under two fermentation modes: steam salt-alkali filtered enzymatic hydrolysate (SSA-F), steam salt-alkali unfiltered (SSA-U), microwave salt-alkali filtered (MSA-F) and microwave salt-alkali unfiltered (MSA-U). The kinetic coefficients were determined by fitting the Monod, modified Gompertz and logistic models to the experimental data with high coefficients of determination R2 > 0.97. A maximum specific growth rate (μ max ) of 0.153 h-1 was obtained under SSA-F and SSA-U whereas, 0.150 h-1 was observed with MSA-F and MSA-U. SSA-U gave a potential maximum bioethanol concentration (Pm) of 31.06 g/L compared to 30.49, 23.26 and 21.79 g/L for SSA-F, MSA-F and MSA-U respectively. An insignificant difference was observed in the μ max and P m for the filtered and unfiltered enzymatic hydrolysate for both SSA and MSA pretreatments, thus potentially reducing a unit operation. These findings provide significant insights for process scale up.
Keywords: Fermentation kinetics; Inorganic salt pretreatment; Lignocellulosic bioethanol; Microwave pretreatment; Sugarcane.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Microwave-assisted inorganic salt pretreatment of sugarcane leaf waste: Effect on physiochemical structure and enzymatic saccharification.Bioresour Technol. 2017 Jul;235:35-42. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2017.03.031. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Bioresour Technol. 2017. PMID: 28360018
-
Simultaneous saccharification and bioethanol production from corn cobs: Process optimization and kinetic studies.Bioresour Technol. 2018 Aug;262:32-41. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.056. Epub 2018 Apr 17. Bioresour Technol. 2018. PMID: 29689438
-
Bioethanol production from sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) plant residue by combined physical, microbial and chemical pretreatments.Bioresour Technol. 2020 Feb;297:122484. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122484. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Bioresour Technol. 2020. PMID: 31810734
-
Progress in the development of alkali and metal salt catalysed lignocellulosic pretreatment regimes: Potential for bioethanol production.Bioresour Technol. 2020 Aug;310:123372. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123372. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Bioresour Technol. 2020. PMID: 32312596 Review.
-
An overview of key pretreatment processes for biological conversion of lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol.3 Biotech. 2015 Oct;5(5):597-609. doi: 10.1007/s13205-015-0279-4. Epub 2015 Feb 3. 3 Biotech. 2015. PMID: 28324530 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sustainable Production of Bioethanol Using Levulinic Acid Pretreated Sawdust.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Jun 30;10:937838. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.937838. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35845396 Free PMC article.
-
Xylooligosaccharides produced from sugarcane leaf arabinoxylan using xylanase from Aureobasidium pullulans NRRL 58523 and its prebiotic activity toward Lactobacillus spp.Heliyon. 2023 Nov 7;9(11):e22107. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e22107. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38034795 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of pretreatment strategies on halophyte Atriplex crassifolia to improve saccharification using thermostable cellulases.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Feb 21;11:1135424. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1135424. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36896009 Free PMC article.
-
Optimization and Scale-Up of Fermentation Processes Driven by Models.Bioengineering (Basel). 2022 Sep 14;9(9):473. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering9090473. Bioengineering (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36135019 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethanol production from lignocellulosic waste materials: kinetics and optimization studies.RSC Adv. 2025 Jul 22;15(32):26091-26103. doi: 10.1039/d5ra02272j. eCollection 2025 Jul 21. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40697482 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zabed H., Sahu J.N., Boyce A.N., Faruq G. Fuel ethanol production from lignocellulosic biomass: an overview on feedstocks and technological approaches. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016;66:751–774.
-
- Chng L.M., Lee K.T., Chan D.J.C. Synergistic effect of pretreatment and fermentation process on carbohydrate-rich Scenedesmus dimorphus for bioethanol production. Energy Convers. Manage. 2017;141:410–419.
-
- Akhtar N., Goyal D., Goyal A. Characterization of microwave-alkali-acid pre-treated rice straw for optimization of ethanol production via simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF) Energy Convers. Manage. 2016
-
- Franko B., Galbe M., Wallberg O. Bioethanol production from forestry residues: a comparative techno-economic analysis. Appl. Energy. 2016;184:727–736.
-
- Dominguez-Bocanegra A.R., Torres-Munoz J.A., Lopez R.A. Production of bioethanol from agro-industrial wastes. Fuel. 2015;149:85–89.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
