Influence of analytic techniques on comparing DTI-derived measurements in early stage Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 31008407
- PMCID: PMC6458486
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01481
Influence of analytic techniques on comparing DTI-derived measurements in early stage Parkinson's disease
Abstract
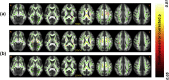
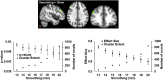
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) studies in early Parkinson's disease (PD) to understand pathologic changes in white matter (WM) organization are variable in their findings. Evaluation of different analytic techniques frequently employed to understand the DTI-derived change in WM organization in a multisite, well-characterized, early stage PD cohort should aid the identification of the most robust analytic techniques to be used to investigate WM pathology in this disease, an important unmet need in the field. Thus, region of interest (ROI)-based analysis, voxel-based morphometry (VBM) analysis with varying spatial smoothing, and the two most widely used skeletonwise approaches (tract-based spatial statistics, TBSS, and tensor-based registration, DTI-TK) were evaluated in a DTI dataset of early PD and Healthy Controls (HC) from the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) cohort. Statistical tests on the DTI-derived metrics were conducted using a nonparametric approach from this cohort of early PD, after rigorously controlling for motion and signal artifacts during DTI scan which are frequent confounds in this disease population. Both TBSS and DTI-TK revealed a significantly negative correlation of fractional anisotropy (FA) with disease duration. However, only DTI-TK revealed radial diffusivity (RD) to be driving this FA correlation with disease duration. HC had a significantly positive correlation of MD with cumulative DaT score in the right middle-frontal cortex after a minimum smoothing level (at least 13mm) was attained. The present study found that scalar DTI-derived measures such as FA, MD, and RD should be used as imaging biomarkers with caution in early PD as the conclusions derived from them are heavily dependent on the choice of the analysis used. This study further demonstrated DTI-TK may be used to understand changes in DTI-derived measures with disease progression as it was found to be more accurate than TBSS. In addition, no singular region was identified that could explain both disease duration and severity in early PD. The results of this study should help standardize the utilization of DTI-derived measures in PD in an effort to improve comparability across studies and time, and to minimize variability in reported results due to variation in techniques.
Keywords: Neuroscience.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of diffusion tensor imaging and fractional anisotropy in the evaluation of patients with idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a literature review.Neurosurg Focus. 2016 Sep;41(3):E12. doi: 10.3171/2016.6.FOCUS16192. Neurosurg Focus. 2016. PMID: 27581308 Review.
-
Progressive Decline in Gray and White Matter Integrity in de novo Parkinson's Disease: An Analysis of Longitudinal Parkinson Progression Markers Initiative Diffusion Tensor Imaging Data.Front Aging Neurosci. 2018 Oct 8;10:318. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00318. eCollection 2018. Front Aging Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30349475 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging of nigral degeneration in Parkinson's disease: A region-of-interest and voxel-based study at 3 T and systematic review with meta-analysis.Neuroimage Clin. 2013 Oct 14;3:481-8. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2013.10.006. eCollection 2013. Neuroimage Clin. 2013. PMID: 24273730 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellar and cerebral white matter changes in Parkinson's disease with resting tremor.Neuroradiology. 2023 Oct;65(10):1497-1506. doi: 10.1007/s00234-023-03206-w. Epub 2023 Aug 7. Neuroradiology. 2023. PMID: 37548715
-
Assessing White Matter Pathology in Early-Stage Parkinson Disease Using Diffusion MRI: A Systematic Review.Front Neurol. 2020 May 14;11:314. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00314. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32477235 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Stability Evaluation of Brain Changes in Parkinson's Disease Based on Machine Learning.Front Comput Neurosci. 2021 Oct 26;15:735991. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2021.735991. eCollection 2021. Front Comput Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34795570 Free PMC article.
-
Unique white matter structural connectivity in early-stage drug-naive Parkinson disease.Neurology. 2020 Feb 25;94(8):e774-e784. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008867. Epub 2019 Dec 27. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 31882528 Free PMC article.
-
Whole brain atlas-based diffusion kurtosis imaging parameters for evaluation of minimal hepatic encephalopathy.Neuroradiol J. 2022 Feb;35(1):67-76. doi: 10.1177/19714009211026924. Epub 2021 Jun 29. Neuroradiol J. 2022. PMID: 34187242 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment of Dementia With Bosutinib: An Open-Label Study of a Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor.Neurol Clin Pract. 2021 Jun;11(3):e294-e302. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000000918. Neurol Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 34484904 Free PMC article.
-
Cingulum and Uncinate Fasciculus Microstructural Abnormalities in Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review of Diffusion Tensor Imaging Studies.Biology (Basel). 2023 Mar 20;12(3):475. doi: 10.3390/biology12030475. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36979166 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

