Harnessing Clinical Sequencing Data for Survival Stratification of Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinomas
- PMID: 31008437
- PMCID: PMC6474404
- DOI: 10.1200/PO.18.00307
Harnessing Clinical Sequencing Data for Survival Stratification of Patients with Metastatic Lung Adenocarcinomas
Abstract
Purpose: Broad panel sequencing of tumors facilitates routine care of people with cancer as well as clinical trial matching for novel genome-directed therapies. We sought to extend the use of broad panel sequencing results to survival stratification and clinical outcome prediction.
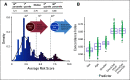
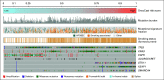
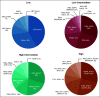
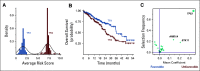
Patients and methods: Using sequencing results from a cohort of 1,054 patients with advanced lung adenocarcinomas, we developed OncoCast, a machine learning tool for survival risk stratification and biomarker identification.
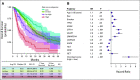
Results: With OncoCast, we stratified this patient cohort into four risk groups based on tumor genomic profile. Patients whose tumors harbored a high-risk profile had a median survival of 7.3 months (95% CI 5.5-10.9), compared to a low risk group with a median survival of 32.8 months (95% CI 26.3-38.5), with a hazard ratio of 4.6 (P<2e-16), far superior to any individual gene predictor or standard clinical characteristics. We found that co-mutations of both STK11 and KEAP1 are a strong determinant of unfavorable prognosis with currently available therapies. In patients with targetable oncogenes including EGFR/ALK/ROS1 and received targeted therapies, the tumor genetic background further differentiated survival with mutations in TP53 and ARID1A contributing to a higher risk score for shorter survival.
Conclusion: Mutational profile derived from broad-panel sequencing presents an effective genomic stratification for patient survival in advanced lung adenocarcinoma. OncoCast is available as a public resource that facilitates the incorporation of mutational data to predict individual patient prognosis and compare risk characteristics of patient populations.
Keywords: Metastatic lung adenocarcinoma; mutational profiling; prognostic model.
Conflict of interest statement
Ronglai Shen
Matthew Hellmann
Kathryn C. Arbour
Ryan Ptashkin
Mark G. Kris
Charles M. Rudin
Michael F. Berger
David B. Solit
Maria Arcila
Marc Ladanyi
Gregory J. Riely
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

