Risk factors of malignant fluorodeoxyglucose-avid lymph node on preablation positron emission tomography in patients with papillary thyroid cancer undergoing radioiodine ablation therapy
- PMID: 31008921
- PMCID: PMC6494284
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014858
Risk factors of malignant fluorodeoxyglucose-avid lymph node on preablation positron emission tomography in patients with papillary thyroid cancer undergoing radioiodine ablation therapy
Abstract
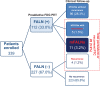
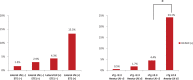
F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)-avid metastatic lesions are associated with a poor response to radioiodine ablation therapy (RIT) in papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). This study evaluated the significance of preablative FDG positron emission tomography (PET) for the assessment of risk factors and frequency of malignant FDG-avid lymph nodes in patients with PTC undergoing RIT.The study included 339 consecutive patients (mean age 46.3 ± 12.5 y; 260 females) with PTC referred for the first RIT and who underwent routine preablative FDG PET between April 2011 and February 2013. FDG-avid lymph nodes (FALNs) were identified using retrospective image reviews. The frequency of malignant FALN (mFALN), its contribution to persistent or recurrent PTC, and its risk factors were analyzed.Among the patients, 112 had FALNs (33.0%): 11 mFALNs (3.2%) and 101 benign FALNs (bFALNs, 29.8%). mFALN contributed to 55% of persistent or recurrent PTC after RIT, which was observed in 20 of 339 patients (5.9%) during the post-RIT follow-up. Among preoperative risk factors, suspicious extrathyroidal extension and lateral neck lymph node metastasis on imaging studies were associated with mFALN. Among postoperative risk factors, T3/T4 and N1b stages, higher stimulated thyroglobulin, and higher numbers of metastatic lymph nodes and dissected lymph nodes, were associated with mFALN.mFALNs were observed in a small number of patients with PTC undergoing RIT, but it contributed 55% of total recurrent or persistent disease. Increased frequency of mFALNs is associated with more advanced PTC. Preablative FDG PET has value in evaluation of patients with RIT-resistant lesions and may help determine further treatment strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PROGNOSTIC VALUE OF LYMPH NODE UPTAKE ON PRETREATMENT F-18 FDG PET/CT IN PATIENTS WITH N1B PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA.Endocr Pract. 2019 Aug;25(8):787-793. doi: 10.4158/EP-2018-0607. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Endocr Pract. 2019. PMID: 31013158
-
Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography scan-positive recurrent papillary thyroid cancer and the prognosis and implications for surgical management.World J Surg Oncol. 2012 Sep 17;10:192. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-10-192. World J Surg Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22985118 Free PMC article.
-
Preablative Stimulated Thyroglobulin Levels Can Predict Malignant Potential and Therapeutic Responsiveness of Subcentimeter-Sized, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-Avid Cervical Lymph Nodes in Patients With Papillary Thyroid Cancer.Clin Nucl Med. 2016 Jan;41(1):e32-8. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000000889. Clin Nucl Med. 2016. PMID: 26164179
-
Respective roles of thyroglobulin, radioiodine imaging, and positron emission tomography in the assessment of thyroid cancer.Semin Nucl Med. 2006 Jul;36(3):194-205. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2006.03.002. Semin Nucl Med. 2006. PMID: 16762610 Review.
-
PANCREAS METASTASES FROM PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE.Endocr Pract. 2017 Dec;23(12):1425-1429. doi: 10.4158/EP-2017-0001. Epub 2017 Nov 16. Endocr Pract. 2017. PMID: 29144798 Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of 18F-FDG PET/CT in Patients with Recurrent Differentiated Thyroid Cancer.Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2021 Oct 15;30(3):137-143. doi: 10.4274/mirt.galenos.2021.02360. Mol Imaging Radionucl Ther. 2021. PMID: 34658228 Free PMC article.
-
KSNM60 in Nuclear Endocrinology: from the Beginning to the Future.Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022 Feb;56(1):17-28. doi: 10.1007/s13139-021-00728-0. Epub 2022 Jan 24. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35186157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of Thymidine Kinase 1 Suppresses Cell Proliferation, Invasion, Migration, and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Thyroid Carcinoma Cells.Front Oncol. 2020 Jan 29;9:1475. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01475. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32064235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maxon HR, 3rd, Englaro EE, Thomas SR, et al. Radioiodine-131 therapy for well-differentiated thyroid cancer--a quantitative radiation dosimetric approach: outcome and validation in 85 patients. J Nucl Med 1992;33:1132–6. - PubMed
-
- Maxon HR, Thomas SR, Hertzberg VS, et al. Relation between effective radiation dose and outcome of radioiodine therapy for thyroid cancer. N Engl J Med 1983;309:937–41. - PubMed
-
- Jung YH, Hah JH, Sung MW, et al. Reciprocal immunohistochemical expression of sodium/iodide symporter and hexokinase I in primary thyroid tumors with synchronous cervical metastasis. Laryngoscope 2009;119:541–8. - PubMed
-
- Min JJ, Chung JK, Lee YJ, et al. Relationship between expression of the sodium/iodide symporter and I-131 uptake in recurrent lesions of differentiated thyroid carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med 2001;28:639–45. - PubMed
-
- Som P, Atkins HL, Bandoypadhyay D, et al. A fluorinated glucose analog, 2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose (F-18): nontoxic tracer for rapid tumor detection. J Nucl Med 1980;21:670–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

