General anesthesia vs spinal anesthesia for patients undergoing total-hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 31008923
- PMCID: PMC6494405
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014925
General anesthesia vs spinal anesthesia for patients undergoing total-hip arthroplasty: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The optimal anesthetic technique remains debated in patients undergoing total-hip arthroplasty (THA). The purpose of this meta-analysis was to test the efficacy of general and spinal anesthesia for patients undergoing THA.
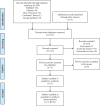
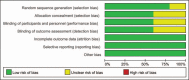
Methods: In January 2018, we searched PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, and the Google database. Data from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the use of general and spinal anesthesia for patients undergoing THA were retrieved. The primary outcome was to compare the total blood loss. The secondary outcomes were the occurrence of deep venous thrombosis (DVT), the occurrence of nausea, and the length of hospital stay. Software Stata 12.0 was used for meta-analysis.
Results: Five RCTs with 487 THAs were finally included for meta-analysis. There was no significant difference between the general anesthesia and spinal anesthesia in terms of the total blood loss (weighted mean difference [WMD] = -20.72, 95% confidence interval [CI] -84.50 to 43.05, P = .524; I = 87.8%) and the occurrence of DVT (risk ratio (RR) = 0.85, 95% CI 0.24-3.01, P = .805; I = 70.5%). Compared with general anesthesia, spinal anesthesia was a significant reduction in the occurrence of nausea (RR = 3.04, 95% CI 1.69-5.50, P = .000; I = 0.0%) and the length of hospital stay (WMD = 1.00, 95% CI 0.59-1.41, P = .000; I = 94.7%).
Conclusion: Spinal anesthesia was superior than general anesthesia in terms of the occurrence of nausea and shorten the length of hospital stay. The quality and number of included studies was limited; thus, a greater number of high-quality RCTs is still needed to further identify the effects of spinal anesthesia on reducing the blood loss after THA.
Figures





References
-
- Kearns R, Macfarlane A, Grant A, et al. A randomised, controlled, double blind, non-inferiority trial of ultrasound-guided fascia iliaca block vs. spinal morphine for analgesia after primary hip arthroplasty. Anaesthesia 2016;71:1431–40. - PubMed
-
- Harsten A, Kehlet H, Ljung P, et al. Total intravenous general anaesthesia vs. spinal anaesthesia for total hip arthroplasty: a randomised, controlled trial. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 2015;59:298–309. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

