Platelet-rich plasma injection for the treatment of chronic Achilles tendinopathy: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 31008973
- PMCID: PMC6494278
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015278
Platelet-rich plasma injection for the treatment of chronic Achilles tendinopathy: A meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is used as an alternative therapy to reduce pain and improve functional restoration in patients with Achilles tendinopathy (AT). We evaluated the current evidence for the efficacy of PRP as a treatment for chronic AT.
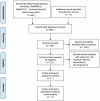
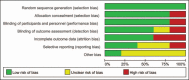
Methods: The PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and The Cochrane Library databases were searched for articles on randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared the efficacy of PRP with that of with placebo injections plus eccentric training as treatment for AT. The articles were uploaded over the establishment of the databases to May 01, 2018. The Cochrane risk of bias (ROB) tool was used to assess methodological quality. Outcome measurements included the Victorian Institute of Sports Assessment-Achilles (VISA-A), visual analog scale (VAS) and Achilles tendon thickness. Statistical analysis was performed with RevMan 5.3.5 software.
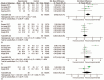
Results: Five RCTs (n = 189) were included in this meta-analysis. Significant differences in the VISA-A were not observed between the PRP and placebo groups after 12 weeks [standardized mean difference (SMD) = 0.2, 95% confidence interval (95% CI): 0.36 to 0.76, I = 71%], 24 weeks (SMD = 0.77, 95% CI: -0.10-1.65, I = 85%) and 1 year (SMD = 0.83, 95% CI: -0.76-2.42, I = 72%) of treatment. However, PRP exhibited better efficacy than the placebo treatment after 6 weeks (SMD = 0.46, 95% CI: 0.15-0.77, I = 34%). Two studies included VAS scores and tendon thickness. VAS scores after 6 weeks (SMD = 1.35, 95% CI: -0.1.04-3.74, I = 93%) and 24 weeks (SMD = 1.48, 95% CI: -0.1.59-4.55, I = 95%) were not significantly different. However, VAS scores at the 12th week (SMD = 1.10, 95% CI: 0.53-1.68, I = 83%) and tendon thickness (SMD = 1.51, 95% CI: 0.39-2.63, I = 53%) were significantly different.
Conclusion: PRP injection around the Achilles tendon is an option for the treatment of chronic AT. Limited evidence supports the conclusion that PRP is not superior to placebo treatment. These results still require verification by a large number of well designed, heterogeneous RCT studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


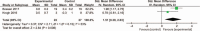
References
-
- McClinton S, Luedke L, Clewley D. Nonsurgical management of midsubstance Achilles tendinopathy. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 2017;34:137–60. - PubMed
-
- Abbassian A, Khan R. Achilles tendinopathy: pathology and management strategies. Br J Hosp Med (Lond) 2009;70:519–23. - PubMed
-
- Wetke E, Johannsen F, Langberg H. Achilles tendinopathy: a prospective study on the effect of active rehabilitation and steroid injections in a clinical setting. Scand J Med Sci Sports 2015;25:e392–9. - PubMed
-
- Srivastava P, Aggarwal A. Ultrasound-guided retro-calcaneal bursa corticosteroid injection for refractory Achilles tendinitis in patients with seronegative spondyloarthropathy: efficacy and follow-up study. Rheumatol Int 2016;36:875–80. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

