Endovascular treatment of a ruptured thoracic aortic pseudoaneurysm secondary to Pott disease during a spine surgery: A case report and a literature review
- PMID: 31008983
- PMCID: PMC6494369
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015306
Endovascular treatment of a ruptured thoracic aortic pseudoaneurysm secondary to Pott disease during a spine surgery: A case report and a literature review
Abstract
Rationale: The coexistence of a tuberculous aortic pseudoaneurysm and Pott disease in patients with a history of tuberculosis (TB) is relatively rare, and the treatment strategies remain still controversial.
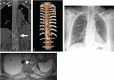
Patient concerns: A 57-year-old female patient with a history of primary pulmonary TB presented with symptoms of breathlessness, chest pain, weight loss, and fever. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT) showed a thoracic aortic pseudoaneurysm secondary to Pott disease at T11/12 level.
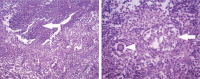
Diagnoses: Tuberculous pseudoaneurysm at the descending thoracic aorta associated with tuberculous vertebral osteomyelitis.
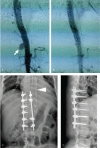
Interventions: We originally planned a combined surgery consisting of posterior spine stabilization, anterior excision of the infected field, and aortic reconstruction. When we surgically stabilized the posterior spine, unexpectedly, the pseudoaneurysm ruptured. Immediately, we terminated the surgery and appropriately placed an endovascular stent graft, which successfully rescued the patient.
Outcomes: When the patient's conditions were stable, we anteriorly debrided all infected tissues and then performed a spinal fusion by grafting autologous iliac bone. After the debridement and spinal fusion, we arranged a 1-year anti-tuberculous chemotherapy for this patient and performed a 24-month follow-up. This patient had no signs of recurrent infection during the follow-up.
Lessons: For the patients with tuberculous aortic aneurysm(s) complicated with vertebral osteomyelitis, the endovascular repair of an aneurysm(s) should be considered a conventional therapy before the spine surgery, lowering the risk of aortic aneurysm rupture. Meanwhile, minimally invasive endovascular stent graft combined with anti-tuberculosis drugs may be considered one of the therapeutic regimens for the patients whose conditions are not suitable for open surgery, such as age, weakness, or severe organ failure.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Tuberculous Thoracic Aortic Pseudoaneurysm Associated With Spinal Tuberculosis: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 26;9:882697. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.882697. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721076 Free PMC article.
-
Endovascular stent graft placement in the treatment of a ruptured tuberculous pseudoaneurysm of the descending thoracic aorta secondary to Pott's disease of the spine.J Card Surg. 2012 Jan;27(1):75-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-8191.2011.01343.x. Epub 2011 Nov 14. J Card Surg. 2012. PMID: 22081927 Review.
-
Treatment of tuberculous aortic pseudoaneurysm associated with vertebral tuberculosis: A case series and a literature review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Apr;97(15):e0382. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010382. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29642195 Free PMC article.
-
Successful treatment of a tuberculous vertebral osteomyelitis eroding the thoracoabdominal aorta: a case report.J Vasc Surg. 2005 Nov;42(5):1010-3. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2005.07.011. J Vasc Surg. 2005. PMID: 16275463
-
Endovascular stent grafting and open surgical replacement for chronic thoracic aortic aneurysms: a systematic review and prospective cohort study.Health Technol Assess. 2022 Jan;26(6):1-166. doi: 10.3310/ABUT7744. Health Technol Assess. 2022. PMID: 35094747
Cited by
-
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair for aortobronchial fistula: a case series.Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2020 Oct 19;4(6):1-6. doi: 10.1093/ehjcr/ytaa265. eCollection 2020 Dec. Eur Heart J Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 34109286 Free PMC article.
-
Infected Aortic Aneurysm with Infective Spondylitis in a Patient with Pre-Aortic Confluence of the Iliac Veins: An Unusual Triple Combination.Vasc Specialist Int. 2021 Dec 29;37:41. doi: 10.5758/vsi.210066. Vasc Specialist Int. 2021. PMID: 34963675 Free PMC article.
-
Tuberculous Aortic Aneurysm - A Review.Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 May 23;37(3):385-393. doi: 10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0611. Braz J Cardiovasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 35605220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tuberculous Thoracic Aortic Pseudoaneurysm Associated With Spinal Tuberculosis: A Case Report and Literature Review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 May 26;9:882697. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.882697. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35721076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nussbaum ES, Rockswold GL, Bergman TA, et al. Spinal tuberculosis: a diagnostic and management challenge. J Neurosurg 1995;83:243–7. - PubMed
-
- Jain AK. Tuberculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2010;92:905–13. - PubMed
-
- Huang B, Li CQ, Liu T, et al. Primary non-Hodgkin's lymphoma of the lumbar vertebrae mimicking tuberculous spondylitis: a case report. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2009;129:1621–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

