Patient-tailored FOLFIRINOX as first line treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 31008993
- PMCID: PMC6494255
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015341
Patient-tailored FOLFIRINOX as first line treatment of patients with advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma
Abstract
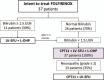
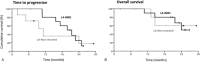
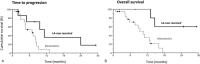
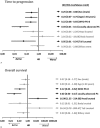
FOLFIRINOX is one of the most effective reference regimens in the 1st line treatment of locally advanced (LA) and metastatic pancreatic cancer (mPC), despite its high toxicity. We evaluated our real-life experience with "patient-tailored intent to treat FOLFIRINOX" in patients with LA or mPC compared to other reports along with the pivotal phase III trial.We analyzed data from all consecutive patients with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma treated with dose-modified FOLFIRINOX in 2016 at Paul Brousse University Hospital. Irinotecan was administered whenever initial serum bilirubin was <1.5 × upper limit of normal. Oxaliplatin was stopped for severe sensory neuropathy. Initial dose reductions were made according to patient profile (eg, age, comorbidities) and later due to toxicity. The treatment was continued until surgery or disease progression. Endpoints were time to progression (TTP), overall survival (OS), objective response rate (ORR), and secondary complete resection (R0R1).Thirty-seven patients with unresectable LA or mPC received patient-tailored FOLFIRINOX as 1st line chemotherapy. There were 22 male (59%) and 15 female patients (41%) aged 44 to 81 years with LA (18 patients, 49%) and mPC (19 patients, 51%). They had World Health Organization-performance status of 0 (59%) or 1 (41%). A total of 384 cycles were administered. Median dose intensities (mg/m/w) were 28.9 for oxaliplatin, 56.8 for irinotecan, and 886.2 for 5-fluorouracil. Thirty-four patients were assessed for response; ORR and disease control rates were 47% and 85%, respectively. R0R1 rate was 30%. Median TTP and OS were 9.6 and 14.6 months. LA disease was associated with significantly longer TTP and OS (P < .001).FOLFIRINOX with patient-tailored dose adaptations seems to offer better results in patients with advanced PC. This approach in the neoadjuvant setting results in a macroscopic R0R1 in 61% of patients with initially unresectable disease. It deserves prospective evaluation to further improve outcomes in the management of advanced PC.
Conflict of interest statement
All of the authors have no conflicts of interest or a source of funding relevant to this article.
Figures
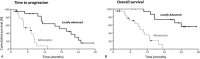
References
-
- Li BR, Hu LH, Li ZS. Chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2014;147:541–2. - PubMed
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Sant M, Allemani C, Santaquilani M, et al. EUROCARE-4. Survival of cancer patients diagnosed in 1995–1999. Results and commentary. Eur J Cancer 2009;45:931–91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

