Plasma Free Cortisol in States of Normal and Altered Binding Globulins: Implications for Adrenal Insufficiency Diagnosis
- PMID: 31009049
- PMCID: PMC6735741
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2019-00022
Plasma Free Cortisol in States of Normal and Altered Binding Globulins: Implications for Adrenal Insufficiency Diagnosis
Abstract
Context: Accurate diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency is critical because there are risks associated with overdiagnosis and underdiagnosis. Data using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) free cortisol (FC) assays in states of high or low cortisol-binding globulin (CBG) levels, including cirrhosis, critical illness, and oral estrogen use, are needed.
Design: Cross-sectional.
Objective: Determine the relationship between CBG and albumin as well as total cortisol (TC) and FC in states of normal and abnormal CBG. Establish the FC level by LC/MS/MS that best predicts TC of <18 μg/dL (497 nmol/L) (standard adrenal insufficiency diagnostic cutoff) in healthy individuals.
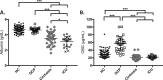
Subjects: This study included a total of 338 subjects in four groups: healthy control (HC) subjects (n = 243), patients with cirrhosis (n = 38), intensive care unit patients (ICU) (n = 26), and oral contraceptive (OCP) users (n = 31).
Main outcome measure(s): FC and TC by LC/MS/MS, albumin by spectrophotometry, and CBG by ELISA.
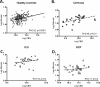
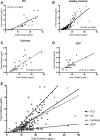
Results: TC correlated with FC in the ICU (R = 0.91), HC (R = 0.90), cirrhosis (R = 0.86), and OCP (R = 0.70) groups (all P < 0.0001). In receiver operator curve analysis in the HC group, FC of 0.9 μg/dL (24.8 nmol/L) predicted TC of <18 μg/dL (497 nmol/L; 98% sensitivity, 91% specificity; AUC, 0.98; P < 0.0001). Decreasing the cutoff to 0.7 μg/dL led to a small decrease in sensitivity (92%) with similar specificity (91%).
Conclusions: A cutoff FC of <0.9 μg/dL (25 nmol/L) in this LC/MS/MS assay predicts TC of <18 μg/dL (497 nmol/L) with excellent sensitivity and specificity. This FC cutoff may be helpful in ruling out adrenal insufficiency in patients with binding globulin derangements.
Copyright © 2019 Endocrine Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
High prevalence of "biochemical" adrenal insufficiency in thalassemics: is it a matter of different testings or decreased cortisol binding globulin?J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010 Oct;95(10):4609-15. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-0205. Epub 2010 Jul 21. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010. PMID: 20660038 Clinical Trial.
-
Cosyntropin-Stimulated Serum Free Cortisol in Healthy, Adrenally Insufficient, and Mildly Cirrhotic Populations.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 Mar;101(3):1075-81. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-2285. Epub 2015 Dec 8. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 26647150 Free PMC article.
-
Minding the gap between cortisol levels measured with second-generation assays and current diagnostic thresholds for the diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency: a single-center experience.Hormones (Athens). 2020 Sep;19(3):425-431. doi: 10.1007/s42000-020-00185-y. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Hormones (Athens). 2020. PMID: 32222957 Free PMC article.
-
The role of corticosteroid-binding globulin in the evaluation of adrenal insufficiency.J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018 Jan 26;31(2):107-115. doi: 10.1515/jpem-2017-0270. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2018. PMID: 29194043 Review.
-
Hypothalamic pituitary adrenal function during critical illness: limitations of current assessment methods.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Oct;91(10):3725-45. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-0674. Epub 2006 Aug 1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16882746 Review.
Cited by
-
Reversible suppression of hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis in Addison's disease due to ethinyl oestradiol-induced increase in total cortisol.Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2024 Dec 19;2024(4):e240055. doi: 10.1530/EDM-24-0055. Print 2024 Oct 1. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 39700335 Free PMC article.
-
From liver to hormones: The endocrine consequences of cirrhosis.World J Gastroenterol. 2024 Mar 7;30(9):1073-1095. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1073. World J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38577191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of electro-mechanical uncouplers, hormonal stimulation and pacing rate on the stability and function of cultured rabbit myocardial slices.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 5;12:1363538. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2024.1363538. eCollection 2024. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38646013 Free PMC article.
-
Adrenal Insufficiency in Cirrhosis.J Endocr Soc. 2022 Jul 29;6(10):bvac115. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvac115. eCollection 2022 Oct 1. J Endocr Soc. 2022. PMID: 36033971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oral Contraceptive Disturbed the Recovery of the Adrenal Function after Adrenalectomy in Cushing Syndrome.Intern Med. 2021 Mar 15;60(6):901-903. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.5462-20. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Intern Med. 2021. PMID: 33055479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hamrahian AH, Oseni TS, Arafah BM. Measurements of serum free cortisol in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. 2004;350(16):1629–1638. - PubMed
-
- Vincent RP, Etogo-Asse FE, Dew T, Bernal W, Alaghband-Zadeh J, le Roux CW. Serum total cortisol and free cortisol index give different information regarding the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis reserve in patients with liver impairment. Ann Clin Biochem. 2009;46(Pt 6):505–507. - PubMed
-
- Tan T, Chang L, Woodward A, McWhinney B, Galligan J, Macdonald GA, Cohen J, Venkatesh B. Characterising adrenal function using directly measured plasma free cortisol in stable severe liver disease. J Hepatol. 2010;53(5):841–848. - PubMed
-
- Galbois A, Rudler M, Massard J, Fulla Y, Bennani A, Bonnefont-Rousselot D, Thibault V, Reignier S, Bourrier A, Poynard T, Thabut D. Assessment of adrenal function in cirrhotic patients: salivary cortisol should be preferred. J Hepatol. 2010;52(6):839–845. - PubMed
-
- Thevenot T, Borot S, Remy-Martin A, Sapin R, Cervoni JP, Richou C, Vanlemmens C, Cleau D, Muel E, Minello A, Tirziu S, Penfornis A, Di Martino V, Monnet E. Assessment of adrenal function in cirrhotic patients using concentration of serum-free and salivary cortisol. Liver Int. 2011;31(3):425–433. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

