Strategies in regulating glioblastoma signaling pathways and anti-invasion therapy
- PMID: 31009513
- PMCID: PMC6476530
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215547
Strategies in regulating glioblastoma signaling pathways and anti-invasion therapy
Abstract
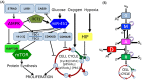
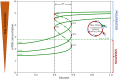
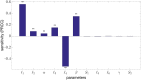
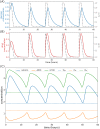
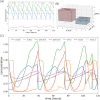
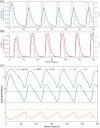
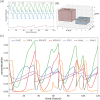
Glioblastoma multiforme is one of the most invasive type of glial tumors, which rapidly grows and commonly spreads into nearby brain tissue. It is a devastating brain cancer that often results in death within approximately 12 to 15 months after diagnosis. In this work, optimal control theory was applied to regulate intracellular signaling pathways of miR-451-AMPK-mTOR-cell cycle dynamics via glucose and drug intravenous administration infusions. Glucose level is controlled to activate miR-451 in the up-stream pathway of the model. A potential drug blocking the inhibitory pathway of mTOR by AMPK complex is incorporated to explore regulation of the down-stream pathway to the cell cycle. Both miR-451 and mTOR levels are up-regulated inducing cell proliferation and reducing invasion in the neighboring tissues. Concomitant and alternating glucose and drug infusions are explored under various circumstances to predict best clinical outcomes with least administration costs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
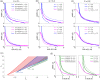
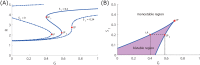
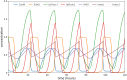
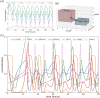
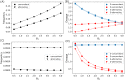
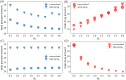
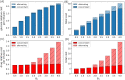
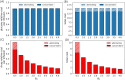
Similar articles
-
Strategies of eradicating glioma cells: a multi-scale mathematical model with MiR-451-AMPK-mTOR control.PLoS One. 2015 Jan 28;10(1):e0114370. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114370. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25629604 Free PMC article.
-
Optimal control strategies of eradicating invisible glioblastoma cells after conventional surgery.J R Soc Interface. 2015 May 6;12(106):20141392. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2014.1392. J R Soc Interface. 2015. PMID: 25833239 Free PMC article.
-
The role of miR-451 in the switching between proliferation and migration in malignant glioma cells: AMPK signaling, mTOR modulation and Rac1 activation required.Int J Oncol. 2017 Jun;50(6):1989-1999. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.3973. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28440461 Free PMC article.
-
The role of octamer binding transcription factors in glioblastoma multiforme.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jun;1859(6):805-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Mar 8. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26968235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Strategies to Discover Effective Drug Targets in Metabolic and Immune Therapy for Glioblastoma.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2017;17(1):17-39. doi: 10.2174/1568009616666160512145436. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2017. PMID: 27562399 Review.
Cited by
-
Optimal regulation of tumour-associated neutrophils in cancer progression.R Soc Open Sci. 2022 Feb 2;9(2):210705. doi: 10.1098/rsos.210705. eCollection 2022 Feb. R Soc Open Sci. 2022. PMID: 35127110 Free PMC article.
-
Collective invasion of glioma cells through OCT1 signalling and interaction with reactive astrocytes after surgery.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020 Sep 14;375(1807):20190390. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2019.0390. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32713306 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin 6 and cancer resistance in glioblastoma multiforme.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Sep 5;47(1):541. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02783-5. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 39231832 Review.
-
Mathematical model of STAT signalling pathways in cancer development and optimal control approaches.R Soc Open Sci. 2021 Sep 29;8(9):210594. doi: 10.1098/rsos.210594. eCollection 2021 Sep. R Soc Open Sci. 2021. PMID: 34631119 Free PMC article.
-
Atorvastatin-mediated rescue of cancer-related cognitive changes in combined anticancer therapies.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 Oct 20;17(10):e1009457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1009457. eCollection 2021 Oct. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 34669701 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

