A pilot metabolomics study of tuberculosis immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
- PMID: 31009738
- PMCID: PMC6613934
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2019.04.015
A pilot metabolomics study of tuberculosis immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome
Abstract
Background: Diagnosis of paradoxical tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (TB-IRIS) is challenging and new tools are needed for early diagnosis as well as to understand the biochemical events that underlie the pathology in TB-IRIS.
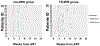
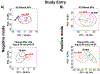
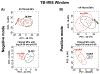
Methods: Plasma samples were obtained from participants from a randomized HIV/TB treatment strategy study (AIDS Clinical Trials Group [ACTG] A5221) with (n = 26) and without TB-IRIS (n = 22) for an untargeted metabolomics pilot study by liquid-chromatography mass spectrometry. The metabolic profile of these participants was compared at the study entry and as close to the diagnosis of TB-IRIS as possible (TB-IRIS window). Molecular features with p < 0.05 and log2 fold change ≥0.58 were submitted for pathway analysis through MetaboAnalyst. We also elucidated potential metabolic signatures for TB-IRIS using a LASSO regression model.
Results: At the study entry, we showed that the arachidonic acid and glycerophospholipid metabolism were altered in the TB-IRIS group. Sphingolipid and linoleic acid metabolism were the most affected pathways during the TB-IRIS window. LASSO modeling selected a set of 8 and 7 molecular features with the potential to predict TB-IRIS at study entry and during the TB-IRIS window, respectively.
Conclusion: This study suggests that the use of plasma metabolites may distinguish HIV-TB patients with and without TB-IRIS.
Keywords: AIDS; Biosignature features; IRIS; Metabolomics; Tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
MD is currently a consultant to Crestone, Inc.
Figures

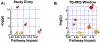
References
-
- Aittokallio T, Schwikowski B. Graph-based methods for analysing networks in cell biology. Brief Bioinform 2006;7(3):243–55. - PubMed
-
- Andrade PR, Pinheiro RO, Sales AM, Illarramendi X, Barbosa MG, Moraes MO, et al. Type 1 reaction in leprosy: a model for a better understanding of tissue immunity under an immunopathological condition. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2015;11(3):391–407. - PubMed
-
- Awodele O, Olayemi SO, Nwite JA, Adeyemo TA. Investigation of the levels of oxidative stress parameters in HIV and HIV-TB co-infected patients.J Infect Dev Ctries 2012;6(1):79–85. - PubMed

