CRAC channels and disease - From human CRAC channelopathies and animal models to novel drugs
- PMID: 31009822
- PMCID: PMC6545165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2019.03.004
CRAC channels and disease - From human CRAC channelopathies and animal models to novel drugs
Abstract
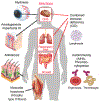
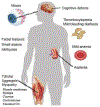
Ca2+ release-activated Ca2+ (CRAC) channels are intimately linked with health and disease. The gene encoding the CRAC channel, ORAI1, was discovered in part by genetic analysis of patients with abolished CRAC channel function. And patients with autosomal recessive loss-of-function (LOF) mutations in ORAI1 and its activator stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) that abolish CRAC channel function and store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) define essential functions of CRAC channels in health and disease. Conversely, gain-of-function (GOF) mutations in ORAI1 and STIM1 are associated with tubular aggregate myopathy (TAM) and Stormorken syndrome due to constitutive CRAC channel activation. In addition, genetically engineered animal models of ORAI and STIM function have provided important insights into the physiological and pathophysiological roles of CRAC channels in cell types and organs beyond those affected in human patients. The picture emerging from this body of work shows CRAC channels as important regulators of cell function in many tissues, and as potential drug targets for the treatment of autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
Keywords: CRAC channel; Calcium; Disease; Immunodeficiency; Mutation; ORAI1; STIM1.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Putney JW Jr., A model for receptor-regulated calcium entry, Cell Calcium, 7 (1986) 1–12. - PubMed
-
- Soboloff J, Romanin C, STIM1 Structure-function and Downstream Signaling Pathways, Cell Calcium, (2019). - PubMed
-
- Feske S, Giltnane J, Dolmetsch R, Staudt LM, Rao A, Gene regulation mediated by calcium signals in T lymphocytes, Nat Immunol, 2 (2001) 316–324. - PubMed
-
- Feske S, Muller JM, Graf D, Kroczek RA, Drager R, Niemeyer C, Baeuerle PA, Peter HH, Schlesier M, Severe combined immunodeficiency due to defective binding of the nuclear factor of activated T cells in T lymphocytes of two male siblings, Eur J Immunol, 26 (1996) 2119–2126. - PubMed
-
- Le Deist F, Hivroz C, Partiseti M, Thomas C, Buc HA, Oleastro M, Belohradsky B, Choquet D, Fischer A, A primary T-cell immunodeficiency associated with defective transmembrane calcium influx, Blood, 85 (1995) 1053–1062. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

