Research progress in the biological activities of 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamic acid (TMCA) derivatives
- PMID: 31009908
- PMCID: PMC7115657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.04.009
Research progress in the biological activities of 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamic acid (TMCA) derivatives
Abstract
TMCA (3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamic acid) ester and amide are privileged structural scaffolds in drug discovery which are widely distributed in natural products and consequently produced diverse therapeutically relevant pharmacological functions. Owing to the potential of TMCA ester and amide analogues as therapeutic agents, researches on chemical syntheses and modifications have been carried out to drug-like candidates with broad range of medicinal properties such as antitumor, antiviral, CNS (central nervous system) agents, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory and hematologic agents for a long time. At the same time, SAR (structure-activity relationship) studies have draw greater attention among medicinal chemists, and many of the lead compounds were derived for various disease targets. However, there is an urgent need for the medicinal chemists to further exploit the precursor in developing chemical entities with promising bioactivity and druggability. This review concisely summarizes the synthesis and biological activity for TMCA ester and amide analogues. It also comprehensively reveals the relationship of significant biological activities along with SAR studies.
Keywords: 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid; Antimicrobial agents; Antitumor agents; Antiviral agents; CNS agnets; Hematologic agents; SAR; TMCA derivatives; anti-inflammatory agents.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures







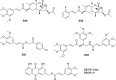
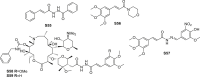
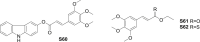
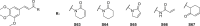


References
-
- Duarte F.S., Marder M., Hoeller A.A., Duzzioni M., Mendes B.G., Pizzolatti M.G., De Lima T.C.M. Anticonvulsant and anxiolytic-like effects of compounds isolated from Polygala sabulosa (Polygalaceae) in rodents: in vitro and in vivo interactions with benzodiazepine binding sites. Psychopharmacology. 2008;197:351–360. - PubMed
-
- Klein L.C., Jr., de Andrade S.F., Cechinel Filho V. A pharmacognostic approach to the Polygala genus: phytochemical and pharmacological aspects. Chem. Biodivers. 2012;9:181–209. - PubMed
-
- Lee C.I., Han J.Y., Hong J.T., Oh K.W. 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid (TMCA), one of the constituents of Polygalae Radix enhances pentobarbital-induced sleeping behaviors via GABAAergic systems in mice. Arch Pharm. Res. (Seoul) 2013;36:1244–1251. - PubMed
-
- Chen C.Y., Wei X.D., Chen C.R. 3,4,5-Trimethoxycinnamic acid, one of the constituents of Polygalae Radix exerts anti-seizure effects by modulating GABAAergic systems in mice. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2016;131:1–5. - PubMed
-
- Jung J.C., Min D., Kim H., Jang S., Lee Y., Park W.K., Khan I.A., Moon H.I., Jung M., Oh S. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl acrylamides as antinarcotic agents. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2010;25:38–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Miscellaneous

