Long-Term Weight Loss With Metformin or Lifestyle Intervention in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study
- PMID: 31009939
- PMCID: PMC6829283
- DOI: 10.7326/M18-1605
Long-Term Weight Loss With Metformin or Lifestyle Intervention in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study
Erratum in
-
Correction: Long-Term Weight Loss With Metformin or Lifestyle Intervention in the Diabetes Prevention Program Outcomes Study.Ann Intern Med. 2020 Sep 15;173(6):508. doi: 10.7326/L20-0029. Ann Intern Med. 2020. PMID: 32926818 No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Identifying reliable predictors of long-term weight loss (LTWL) could lead to improved weight management.
Objective: To identify some predictors of LTWL.
Design: The DPP (Diabetes Prevention Program) was a randomized controlled trial that compared weight loss with metformin, intensive lifestyle intervention (ILS), or placebo. Its Outcomes Study (DPPOS) observed patients after the masked treatment phase ended. (ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT00004992 and NCT00038727).
Setting: 27 DPP and DPPOS clinics.
Participants: Of the 3234 randomly assigned participants, 1066 lost at least 5% of baseline weight in the first year and were followed for 15 years.
Measurements: Treatment assignment, personal characteristics, and weight.
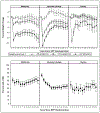
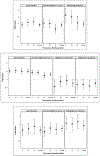
Results: After 1 year, 289 (28.5%) participants in the metformin group, 640 (62.6%) in the ILS group, and 137 (13.4%) in the placebo group had lost at least 5% of their weight. After the masked treatment phase ended, the mean weight loss relative to baseline that was maintained between years 6 and 15 was 6.2% (95% CI, 5.2% to 7.2%) in the metformin group, 3.7% (CI, 3.1% to 4.4%) in the ILS group, and 2.8% (CI, 1.3% to 4.4%) in the placebo group. Independent predictors of LTWL included greater weight loss in the first year in all groups, older age and continued metformin use in the metformin group, older age and absence of either diabetes or a family history of diabetes in the ILS group, and higher fasting plasma glucose levels at baseline in the placebo group.
Limitation: Post hoc analysis; examination of nonrandomized subsets of randomized groups after year 1.
Conclusion: Among persons with weight loss of at least 5% after 1 year, those originally randomly assigned to metformin had the greatest loss during years 6 to 15. Older age and the amount of weight initially lost were the most consistent predictors of LTWL maintenance.
Primary funding source: National Institutes of Health.
Figures
Comment in
-
Advising Patients on How to Achieve Long-Term Weight Loss.Ann Intern Med. 2019 May 21;170(10):724-725. doi: 10.7326/M19-0782. Epub 2019 Apr 23. Ann Intern Med. 2019. PMID: 31009940 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jensen MD, Ryan DH, Apovian CM, Ard JD, Comuzzie AG, Donato KA, et al. 2013 AHA/ACC/TOS Guideline for the Management of Overweight and Obesity in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and The Obesity Society. Circulation. 2014;129(Suppl 2):S102–S38. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tuomilehto J, Lindström J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hämäläinen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, et al. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(18):1343–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- U01 DK048412/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048375/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048434/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048413/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK078907/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM104940/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR016587/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048339/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048443/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048400/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048468/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048404/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048407/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048437/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048406/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048397/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048381/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048514/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048485/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048489/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048349/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK048377/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK017047/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
