From Probiotics to Psychobiotics: Live Beneficial Bacteria Which Act on the Brain-Gut Axis
- PMID: 31010014
- PMCID: PMC6521058
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11040890
From Probiotics to Psychobiotics: Live Beneficial Bacteria Which Act on the Brain-Gut Axis
Abstract
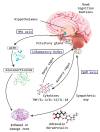
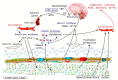
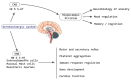
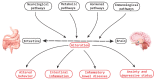
There is an important relationship between probiotics, psychobiotics and cognitive and behavioral processes, which include neurological, metabolic, hormonal and immunological signaling pathways; the alteration in these systems may cause alterations in behavior (mood) and cognitive level (learning and memory). Psychobiotics have been considered key elements in affective disorders and the immune system, in addition to their effect encompassing the regulation of neuroimmune regulation and control axes (the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis or HPA, the sympathetic-adrenal-medullary axis or SAM and the inflammatory reflex) in diseases of the nervous system. The aim of this review is to summarize the recent findings about psychobiotics, the brain-gut axis and the immune system. The review focuses on a very new and interesting field that relates the microbiota of the intestine with diseases of the nervous system and its possible treatment, in neuroimmunomodulation area. Indeed, although probiotic bacteria will be concentrated after ingestion, mainly in the intestinal epithelium (where they provide the host with essential nutrients and modulation of the immune system), they may also produce neuroactive substances which act on the brain-gut axis.
Keywords: beneficial bacteria; human health; microbiota; probiotics; psychobiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

