Theobromine Improves Working Memory by Activating the CaMKII/CREB/BDNF Pathway in Rats
- PMID: 31010016
- PMCID: PMC6520707
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11040888
Theobromine Improves Working Memory by Activating the CaMKII/CREB/BDNF Pathway in Rats
Abstract
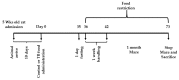
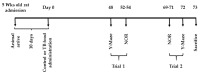
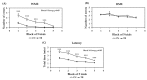
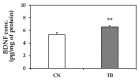
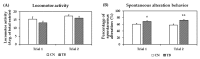
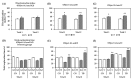
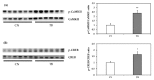
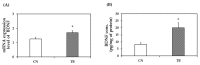
Theobromine (TB) is a primary methylxanthine found in cacao beans. cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) is a transcription factor, which is involved in different brain processes that bring about cellular changes in response to discrete sets of instructions, including the induction of brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF). Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) has been strongly implicated in the memory formation of different species as a key regulator of gene expression. Here we investigated whether TB acts on the CaMKII/CREB/BDNF pathway in a way that might improve the cognitive and learning function in rats. Male Wistar rats (5 weeks old) were divided into two groups. For 73 days, the control rats (CN rats) were fed a normal diet, while the TB-fed rats (TB rats) received the same food, but with a 0.05% TB supplement. To assess the effects of TB on cognitive and learning ability in rats: The radial arm maze task, novel object recognition test, and Y-maze test were used. Then, the brain was removed and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) was isolated for Western Blot, real-time PCR and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Phosphorylated CaMKII (p-CaMKII), phosphorylated CREB (p-CREB), and BDNF level in the mPFC were measured. In all the behavior tests, working memory seemed to be improved by TB ingestion. In addition, p-CaMKII and p-CREB levels were significantly elevated in the mPFC of TB rats in comparison to those of CN rats. We also found that cortical BDNF protein and mRNA levels in TB rats were significantly greater than those in CN rats. These results suggest that orally supplemented TB upregulates the CaMKII/CREB/BDNF pathway in the mPFC, which may then improve working memory in rats.
Keywords: BDNF; CREB; CaMKII; behavior; cacao; theobromine; working memory.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fredholm B.B., Bättig K., Holmén J., Nehlig A., Zvartau E.E. Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999;51:83–133. - PubMed
-
- Miwa S., Sugimoto N., Yamamoto N., Shirai T., Nishida H., Hayashi K., Kimura H., Takeuchi A., Igarashi K., Yachie A., et al. Caffeine induces apoptosis of osteosarcoma cells by inhibiting AKT/mTOR/S6K, NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Anticancer Res. 2012;32:3643–3649. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

