Activity of Selected Nucleoside Analogue ProTides against Zika Virus in Human Neural Stem Cells
- PMID: 31010044
- PMCID: PMC6521205
- DOI: 10.3390/v11040365
Activity of Selected Nucleoside Analogue ProTides against Zika Virus in Human Neural Stem Cells
Abstract
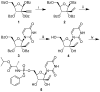
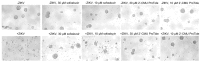
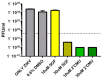
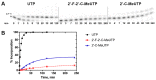
Zika virus (ZIKV), an emerging flavivirus that causes neurodevelopmental impairment to fetuses and has been linked to Guillain-Barré syndrome continues to threaten global health due to the absence of targeted prophylaxis or treatment. Nucleoside analogues are good examples of efficient anti-viral inhibitors, and prodrug strategies using phosphate masking groups (ProTides) have been employed to improve the bioavailability of ribonucleoside analogues. Here, we synthesized and tested a small library of 13 ProTides against ZIKV in human neural stem cells. Strong activity was observed for 2'-C-methyluridine and 2'-C-ethynyluridine ProTides with an aryloxyl phosphoramidate masking group. Substitution of a 2-(methylthio) ethyl phosphoramidate for the aryloxyl phosphoramidate ProTide group of 2'-C-methyluridine completely abolished antiviral activity of the compound. The aryloxyl phosphoramidate ProTide of 2'-C-methyluridine outperformed the hepatitis C virus (HCV) drug sofosbuvir in suppression of viral titers and protection from cytopathic effect, while the former compound's triphosphate active metabolite was better incorporated by purified ZIKV NS5 polymerase over time. These findings suggest both a nucleobase and ProTide group bias for the anti-ZIKV activity of nucleoside analogue ProTides in a disease-relevant cell model.
Keywords: NS5; ProTides; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; Zika virus; antiviral agents; neural stem cells; nucleoside analogues; prodrugs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- De Araújo T.V.B., de Alencar Ximenes R.A., de Barros Miranda-Filho D., Souza W.V., Montarroyos U.R., de Melo A.P.L., Valongueiro S., Braga C., Brandão Filho S.P., Cordeiro M.T., et al. Association between microcephaly, Zika virus infection, and other risk factors in Brazil: Final report of a case-control study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018;18:328–336. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ferrero D., Ferrer-Orta C., Verdaguer N. Viral RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerases: A Structural Overview. Subcell. Biochem. 2018;88:39–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

