Current State and Future Perspectives on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
- PMID: 31010054
- PMCID: PMC6523542
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11040193
Current State and Future Perspectives on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
Abstract
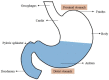
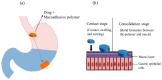
In recent years, many attempts have been made to enhance the drug bioavailability and therapeutic effectiveness of oral dosage forms. In this context, various gastroretentive drug delivery systems (GRDDS) have been used to improve the therapeutic efficacy of drugs that have a narrow absorption window, are unstable at alkaline pH, are soluble in acidic conditions, and are active locally in the stomach. In this review, we discuss the physiological state of the stomach and various factors that affect GRDDS. Recently applied gastrointestinal technologies such as expandable, superporous hydrogel; bio/mucoadhesive, magnetic, ion-exchange resin; and low- and high-density-systems have also been examined along with their merits and demerits. The significance of in vitro and in vivo evaluation parameters of various GRDDS is summarized along with their applications. Moreover, future perspectives on this technology are discussed to minimize the gastric emptying rate in both the fasted and fed states. Overall, this review may inform and guide formulation scientists in designing the GRDDS.
Keywords: bioavailability; gastric retention time; gastroretentive drug delivery systems; narrow absorption window; polymer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lopes C.M., Bettencourt C., Rossi A., Buttini F., Barata P. Overview on gastroretentive drug delivery systems for improving drug bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2016;510:144–158. - PubMed
-
- Rouge N., Buri P., Doelker E. Drug absorption sites in the gastrointestinal tract and dosage forms for site-specific delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 1996;136:117–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(96)85200-8. - DOI
-
- Fujimori J., Machida Y., Tanaka S., Nagai T. Effect of magnetically controlled gastric residence of sustained release tablets on bioavailability of acetaminophen. Int. J. Pharm. 1995;119:47–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-5173(94)00368-F. - DOI
-
- Kim S., Hwang K.-M., Park Y.S., Nguyen T.-T., Park E.-S. Preparation and evaluation of non-effervescent gastroretentive tablets containing pregabalin for once-daily administration and dose proportional pharmacokinetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2018;550:160–169. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2018.08.038. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

