Recognition of Emotion Intensities Using Machine Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study
- PMID: 31010081
- PMCID: PMC6514572
- DOI: 10.3390/s19081897
Recognition of Emotion Intensities Using Machine Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study
Abstract
Over the past two decades, automatic facial emotion recognition has received enormous attention. This is due to the increase in the need for behavioral biometric systems and human-machine interaction where the facial emotion recognition and the intensity of emotion play vital roles. The existing works usually do not encode the intensity of the observed facial emotion and even less involve modeling the multi-class facial behavior data jointly. Our work involves recognizing the emotion along with the respective intensities of those emotions. The algorithms used in this comparative study are Gabor filters, a Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG), and Local Binary Pattern (LBP) for feature extraction. For classification, we have used Support Vector Machine (SVM), Random Forest (RF), and Nearest Neighbor Algorithm (kNN). This attains emotion recognition and intensity estimation of each recognized emotion. This is a comparative study of classifiers used for facial emotion recognition along with the intensity estimation of those emotions for databases. The results verified that the comparative study could be further used in real-time behavioral facial emotion and intensity of emotion recognition.
Keywords: automatic facial emotion recognition; behavioral biometrical systems; intensity of emotion recognition; machine learning.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






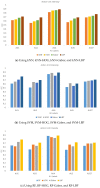
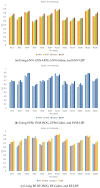
Similar articles
-
CASME II: an improved spontaneous micro-expression database and the baseline evaluation.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 27;9(1):e86041. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086041. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24475068 Free PMC article.
-
A Micro-GA Embedded PSO Feature Selection Approach to Intelligent Facial Emotion Recognition.IEEE Trans Cybern. 2017 Jun;47(6):1496-1509. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2016.2549639. Epub 2016 Apr 21. IEEE Trans Cybern. 2017. PMID: 28113688
-
Robust representation and recognition of facial emotions using extreme sparse learning.IEEE Trans Image Process. 2015 Jul;24(7):2140-52. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2416634. Epub 2015 Mar 25. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2015. PMID: 25823034
-
Random Deep Belief Networks for Recognizing Emotions from Speech Signals.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2017;2017:1945630. doi: 10.1155/2017/1945630. Epub 2017 Mar 5. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28356908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review on Automatic Facial Expression Recognition Systems Assisted by Multimodal Sensor Data.Sensors (Basel). 2019 Apr 18;19(8):1863. doi: 10.3390/s19081863. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31003522 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Facial geometric feature extraction based emotional expression classification using machine learning algorithms.PLoS One. 2021 Feb 18;16(2):e0247131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247131. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33600467 Free PMC article.
-
Emotional Speech Recognition Method Based on Word Transcription.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Mar 2;22(5):1937. doi: 10.3390/s22051937. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35271083 Free PMC article.
-
A Case Study of Facial Emotion Classification Using Affdex.Sensors (Basel). 2019 May 9;19(9):2140. doi: 10.3390/s19092140. Sensors (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31075816 Free PMC article.
-
Smart Sensor Based on Biofeedback to Measure Child Relaxation in Out-of-Home Care.Sensors (Basel). 2020 Jul 28;20(15):4194. doi: 10.3390/s20154194. Sensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32731523 Free PMC article.
-
Emotion and Stress Recognition Related Sensors and Machine Learning Technologies.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Mar 24;21(7):2273. doi: 10.3390/s21072273. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804987 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang L. Behavioral Biometrics for Human Identification: Intelligent Applications: Intelligent Applications. IGI Global; Hershey, PA, USA: 2009.
-
- Gamboa H., Fred A. A behavioral biometric system based on human-computer interaction. Proc. SPIE. 2004;5404:381–393.
-
- Hess U., Banse R., Kappas A. The intensity of facial expression is determined by underlying affective state and social situation. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1995;69:280. doi: 10.1037/0022-3514.69.2.280. - DOI
-
- Bronstein A.M., Bronstein M.M., Kimmel R. International Conference on Audio-and Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2003. Expression-invariant 3D face recognition; pp. 62–70.
-
- Hesher C., Srivastava A., Erlebacher G. A novel technique for face recognition using range imaging; Proceedings of the Seventh International Symposium on Signal Processing and Its Applications; Paris, France. 4 July 2003; pp. 201–204.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

