miR-194 Accelerates Apoptosis of Aβ1⁻42-Transduced Hippocampal Neurons by Inhibiting Nrn1 and Decreasing PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway Activity
- PMID: 31010100
- PMCID: PMC6523401
- DOI: 10.3390/genes10040313
miR-194 Accelerates Apoptosis of Aβ1⁻42-Transduced Hippocampal Neurons by Inhibiting Nrn1 and Decreasing PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway Activity
Abstract
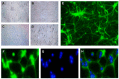
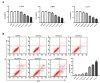
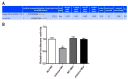
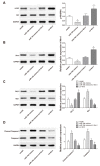
This article explores the mechanism of miR-194 on the proliferation and apoptosis of Aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neurons. Aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neuron model was established by inducing hippocampal neurons with Aβ1-42. MTT assay and flow cytometry were used to detect the viability and apoptosis of hippocampal neurons, respectively. qRT-PCR was used to detect changes in miR-194 and Nrn1 expression after Aβ1-42 induction. Aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neurons were transfected with miR-194 mimics and/or Nrn1 overexpression vectors. Their viability and neurite length were detected by MTT assay and immunofluorescence, respectively. Western blot was used to detect protein expression. Aβ1-42 inhibited Aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neuron activity and promoted their apoptosis in a dose-dependent manner. miR-194 was upregulated and Nrn1 was downregulated in Aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neurons (p < 0.05). Compared with the model group, Aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neurons of the miR-194 mimic group had much lower activity, average longest neurite length, Nrn1, p-AkT, and Bcl-2 protein expression and had much higher Bax, Caspase-3, and Cleaved Caspase-3 protein expression. Compared with the model group, Aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neurons of the LV-Nrn1 group had much higher activity, average longest neurite length, Nrn1, p-AkT, and Bcl-2 protein expression and had much lower Bax, Caspase-3, and Cleaved Caspase-3 protein expression. Nrn1 is a target gene of miR-194. miR-194 inhibited apoptosis of Aβ1-42-transduced hippocampal neurons by inhibiting Nrn1 and decreasing PI3K/AkT signaling pathway activity.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Nrn1; PI3K/AkT signaling pathway; apoptosis; hippocampal neurons; miR-194; proliferation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-25 aggravates Aβ1-42-induced hippocampal neuron injury in Alzheimer's disease by downregulating KLF2 via the Nrf2 signaling pathway in a mouse model.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Sep;120(9):15891-15905. doi: 10.1002/jcb.28861. Epub 2019 May 29. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31144355
-
MicroRNA miR-212 regulates PDCD4 to attenuate Aβ25-35-induced neurotoxicity via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in Alzheimer's disease.Biotechnol Lett. 2020 Sep;42(9):1789-1797. doi: 10.1007/s10529-020-02915-z. Epub 2020 May 30. Biotechnol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32474742
-
Role of miR-211 in a PC12 cell model of Alzheimer's disease via regulation of neurogenin 2.Exp Physiol. 2021 Apr;106(4):1061-1071. doi: 10.1113/EP088953. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Exp Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33527539
-
Ponicidin attenuates Aβ1-42-induced hippocampal cell injury through SIRT1 and PI3K/Akt pathways.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 24;52(1):752. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10854-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40705095
-
Dexmedetomidine improves propofol-induced neuronal injury in rat hippocampus with the involvement of miR-34a and the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Life Sci. 2020 Apr 15;247:117359. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117359. Epub 2020 Jan 27. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32001264
Cited by
-
Effect of circular RNA, mmu_circ_0000296, on neuronal apoptosis in chronic cerebral ischaemia via the miR-194-5p/Runx3/Sirt1 axis.Cell Death Discov. 2021 May 29;7(1):124. doi: 10.1038/s41420-021-00507-y. Cell Death Discov. 2021. PMID: 34052838 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and Therapeutic Prospect of miRNAs in Neurodegenerative Diseases.Behav Neurol. 2023 Nov 23;2023:8537296. doi: 10.1155/2023/8537296. eCollection 2023. Behav Neurol. 2023. PMID: 38058356 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NcRNAs: A synergistically antiapoptosis therapeutic tool in Alzheimer's disease.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Apr;30(4):e14476. doi: 10.1111/cns.14476. Epub 2023 Sep 22. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 37735992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circulating microRNA miR-425-5p Associated with Brain White Matter Lesions and Inflammatory Processes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 10;25(2):887. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020887. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255959 Free PMC article.
-
Alcohol Dehydrogenase 1B Suppresses β-Amyloid-Induced Neuron Apoptosis.Front Aging Neurosci. 2019 Jun 5;11:135. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00135. eCollection 2019. Front Aging Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31231206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Xu J., Begley P., Church S.J., Patassini S., Hollywood K.A., Jüllig M., Curtis M.A., Waldvogel H.J., Faull R.L.M., Unwin R.D. Graded perturbations of metabolism in multiple regions of human brain in Alzheimer’s disease: Snapshot of a pervasive metabolic disorder. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2016;1862:1084–1092. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.03.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Förstl H., Sattel H., Bahro M. Alzheimer’s disease: Clinical features. Int. Rev. Psychiatry. 2009;5:327–349. doi: 10.3109/09540269309037797. - DOI
-
- Kim H.J., Cha J., Lee J.M., Shin J.S., Jung N.Y., Kim Y.J., Choe Y.S., Lee K.H., Kim S.T., Kim J.S. Distinctive Resting State Network Disruptions Among Alzheimer’s Disease, Subcortical Vascular Dementia, and Mixed Dementia Patients. Alzheimers Dement. J. Alzheimers Assoc. 2016;11:P412. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2015.06.375. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Koyama A., Hashimoto M., Tanaka H., Fujise N., Matsushita M., Miyagawa Y., Hatada Y., Fukuhara R., Hasegawa N., Todani S. Malnutrition in Alzheimer’s Disease, Dementia with Lewy Bodies, and Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: Comparison Using Serum Albumin, Total Protein, and Hemoglobin Level. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0157053. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0157053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

