A Water-Soluble Microencapsulated Milk Thistle Extract as Active Ingredient for Dermal Formulations
- PMID: 31010144
- PMCID: PMC6515195
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24081547
A Water-Soluble Microencapsulated Milk Thistle Extract as Active Ingredient for Dermal Formulations
Abstract
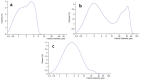
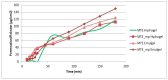
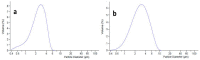
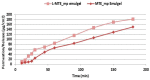
The choice of formulation is often of crucial importance in order to obtain a pharmaceutical product for the administration of poorly soluble drugs. Recently, a new water-soluble microparticulate powder form (MTE-mp) for the oral administration of a high functionality/low solubility silymarin rich milk thistle extract (MTE) has been developed. Findings showed that extract-loaded microparticles by spray-drying were produced with high and reproducible yields and encapsulation efficiency. The in vitro dissolution and permeation rates of silymarin were dramatically improved with respect to the raw material, and also enhanced the silymarin anti-inflammatory abilities. Given these successful results, the new MTE-mp delivery system has been proposed as an active ingredient for dermal applications. The aim of this research was the design and development of two topical formulations, hydrogel and emulgel (O/W emulsion), containing the MTE-mp delivery system or MTE raw extract. All the formulations were compared to each other in terms of handling and incorporation amount of the active ingredient during the productive process. Moreover, the addition to the emulgel of lecithin (L) as enhancer of permeation was tested. The MTE-mp ingredient that resulted was stable and more-easily incorporated both in hydrogel and emulgel than raw MTE extract, obtaining the best permeation profile for MTE-mp from emulgel with the addition of L. The obtained results confirm that the MTE-mp system could be used as a stable, water-soluble, and easy-handling functional ingredient, giving the opportunity to develop new strategies for MTE delivery in health products.
Keywords: delivery system; hydrogel and emulgel; lecithin; silymarin; stability and in vitro permeation profile.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Fehér P., Ujhelyi Z., Váradi J., Fenyvesi F., Róka E., Juhász B., Varga B., Bombicz M., Priksz D., Bácskay I., et al. Efficacy of Pre- and Post-Treatment by Topical Formulations Containing Dissolved and Suspended Silybum marianum against UVB-Induced Oxidative Stress in Guinea Pig and on HaCaT Keratinocytes. Molecules. 2016;21:1269. doi: 10.3390/molecules21101269. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marrow B., Secreted S., Protect C. NIH Public Access. Bone. 2014;71:3831–3840. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-4002.BONE. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

