Effects of Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus on Gut Microbiota in Patients with Lactose Intolerance and Persisting Functional Gastrointestinal Symptoms: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Cross-Over Study
- PMID: 31010241
- PMCID: PMC6520754
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11040886
Effects of Bifidobacterium longum and Lactobacillus rhamnosus on Gut Microbiota in Patients with Lactose Intolerance and Persisting Functional Gastrointestinal Symptoms: A Randomised, Double-Blind, Cross-Over Study
Abstract
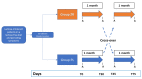
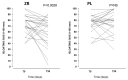
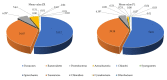
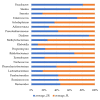
Functional gastrointestinal symptoms are frequent, and may be driven by several pathogenic mechanisms. Symptoms may persist in lactose intolerant (LI) patients (i.e., subjects with intestinal lactase deficiency, lactose malabsorption producing symptoms), after a lactose-free diet. Our hypothesis was that probiotic and vitamin B6 treatment may be useful to alleviate symptoms in LI patients through a positive modulation of gut microbial composition and relative metabolism. We aimed to test the efficacy of a novel formulation of Bifidobacterium longum BB536 and Lactobacillus rhamnosus HN001 plus vitamin B6 (ZR) in 23 LI subjects with persistent symptoms during a lactose-free diet. Symptoms, microbiome, and metabolome were measured at baseline and after 30 days in a crossover, randomized, double-blind study of ZR versus placebo (PL). Compared with PL, the administration of probiotics and vitamin B6 significantly decreased bloating (p = 0.028) and ameliorated constipation (p = 0.045). Fecal microbiome differed between ZR and PL. ZR drove the enrichment of several genera involved in lactose digestion including Bifidobacerium. Moreover, the relative abundance of acetic acid, 2-methyl-propanoic acid, nonenal, and indolizine 3-methyl increased, while phenol decreased. Our findings highlight the importance of selected probiotics and vitamin B6 to alleviate symptoms and gut dysbiosis in lactose intolerant patients with persistent functional gastrointestinal symptoms.
Keywords: lactose intolerance; metabolome; microbiome; probiotics; vitamin B6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

References
-
- Portincasa P., Moschetta A., Baldassarre G., Altomare D.F., Palasciano G. Pan-enteric dysmotility, impaired quality of life and alexithymia in a large group of patients meeting ROME II criteria for irritable bowel syndrome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2003;9:2293–2299. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v9.i10.2293. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liebert A., Lopez S., Jones B.L., Montalva N., Gerbault P., Lau W., Thomas M.G., Bradman N., Maniatis N., Swallow D.M. World-wide distributions of lactase persistence alleles and the complex effects of recombination and selection. Hum. Genet. 2017;136:1445–1453. doi: 10.1007/s00439-017-1847-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

