Effects of cold water immersion and compression garment use after eccentric exercise on recovery
- PMID: 31010274
- PMCID: PMC6477821
- DOI: 10.20463/jenb.2019.0007
Effects of cold water immersion and compression garment use after eccentric exercise on recovery
Abstract
Purpose: The combined effect of different types of post-exercise treatment has not been fully explored. We investigated the effect of combined cold water immersion (CWI) and compression garment (CG) use after maximal eccentric exercise on maximal muscle strength, indirect muscle damage markers in the blood, muscle thickness, and muscle soreness score 24 h after exercise.
Methods: Ten men performed two trials (CWI + CG and CON) in random order. In the CWI + CG trial, the subjects performed 15 min of CWI (15°C), followed by wearing of a lower-body CG for 24 h after exercise. In the CON trial, there was no post-exercise treatment. The exercise consisted of 6 × 10 maximal isokinetic (60°·s-1) eccentric knee extensions using one lower limb. The maximal voluntary contraction (MVC) and maximal isokinetic (60°·s-1) strength during knee extension, as well as the indirect muscle damage markers, were evaluated before exercise and 24 h after exercise.
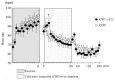
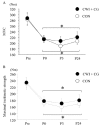
Results: The maximal muscle strength decreased in both trials (p < 0.001), with no difference between them. The exercise-induced elevation in the myoglobin concentration tended to be lower in the CWI + CG trial than in the CON trial (p = 0.060). The difference in the MVC, maximal isokinetic strength, muscle thickness, and muscle soreness score between the trials was not significant.
Conclusion: CWI followed by wearing of a CG after maximal eccentric exercise tended to attenuate the exercise-induced elevation of indirect muscle damage markers in the blood.
Keywords: recovery.
©2019 The Korean Society for Exercise Nutrition.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of cold-water immersion treatment on recovery from exercise-induced muscle damage in the hamstring.Eur J Sport Sci. 2025 Mar;25(3):e12235. doi: 10.1002/ejsc.12235. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Eur J Sport Sci. 2025. PMID: 39665595 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of CO2 and H2 gas mixture in cold water immersion on recovery after eccentric loading.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 21;9(10):e20288. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20288. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37767470 Free PMC article.
-
Dosages of cold-water immersion post exercise on functional and clinical responses: a randomized controlled trial.Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017 Nov;27(11):1356-1363. doi: 10.1111/sms.12734. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Scand J Med Sci Sports. 2017. PMID: 27430594 Clinical Trial.
-
Post-exercise Cold Water Immersion Effects on Physiological Adaptations to Resistance Training and the Underlying Mechanisms in Skeletal Muscle: A Narrative Review.Front Sports Act Living. 2021 Apr 8;3:660291. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2021.660291. eCollection 2021. Front Sports Act Living. 2021. PMID: 33898988 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intramuscular Temperature Changes in the Quadriceps Femoris Muscle After Post-Exercise Cold-Water Immersion (10°C for 10 min): A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis.Front Sports Act Living. 2021 May 6;3:660092. doi: 10.3389/fspor.2021.660092. eCollection 2021. Front Sports Act Living. 2021. PMID: 34027405 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Endocrine and Metabolic Responses to Endurance Exercise Under Hot and Hypoxic Conditions.Front Physiol. 2020 Aug 19;11:932. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00932. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32973541 Free PMC article.
-
Myostatin A55T Genotype is Associated with Strength Recovery Following Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jul 7;17(13):4900. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17134900. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32645967 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Body Fat Percentage on Muscle Damage Induced by High-Intensity Eccentric Exercise.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 16;17(10):3476. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103476. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32429389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hirose L, Nosaka K, Newton M, Laveder A, Kano M, Peake J, Suzuki K. Changes in inflammatory mediators following eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Exerc Immunol Rev. 2004;10:75–95. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

