Interfacial Binding Sites for Cholesterol on G Protein-Coupled Receptors
- PMID: 31010663
- PMCID: PMC6506644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.03.025
Interfacial Binding Sites for Cholesterol on G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Abstract
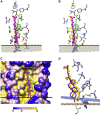
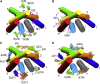
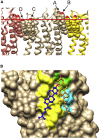
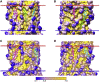
A docking procedure is described that allows the transmembrane surface of a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) to be swept rapidly for potential binding sites for cholesterol at the bilayer interfaces on the two sides of the membrane. The procedure matches 89% of the cholesterols resolved in published GPCR crystal structures, when cholesterols likely to be crystal packing artifacts are excluded. Docking poses are shown to form distinct clusters on the protein surface, the clusters corresponding to "greasy hollows" between protein ridges. Docking poses depend on the angle of tilt of the GPCR in the surrounding lipid bilayer. It is suggested that thermal motion could alter the optimal binding pose for a cholesterol molecule, with the range of binding poses within a cluster providing a guide to the range of thermal motions likely for a cholesterol within a binding site.
Copyright © 2019 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
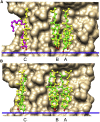
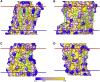
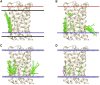
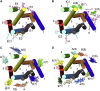
Similar articles
-
Interfacial Binding Sites for Cholesterol on TRP Ion Channels.Biophys J. 2019 Nov 19;117(10):2020-2033. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.10.011. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Biophys J. 2019. PMID: 31672270 Free PMC article.
-
G protein coupled receptor interactions with cholesterol deep in the membrane.Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017 Feb;1859(2):268-281. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2016.12.001. Epub 2016 Dec 3. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 2017. PMID: 27919726
-
Assessing GPCR homology models constructed from templates of various transmembrane sequence identities: Binding mode prediction and docking enrichment.J Mol Graph Model. 2018 Mar;80:38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2017.12.017. Epub 2017 Dec 29. J Mol Graph Model. 2018. PMID: 29306746
-
Molecular dynamics simulations of GPCR-cholesterol interaction: An emerging paradigm.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Sep;1848(9):1775-82. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2015.03.018. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25817549 Review.
-
Are specific nonannular cholesterol binding sites present in G-protein coupled receptors?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009 Feb;1788(2):295-302. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.11.020. Epub 2008 Dec 9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2009. PMID: 19111523 Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial Cell Plasma Membrane Biomechanics Mediates Effects of Pro-Inflammatory Factors on Endothelial Mechanosensors: Vicious Circle Formation in Atherogenic Inflammation.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Feb 10;12(2):205. doi: 10.3390/membranes12020205. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35207126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of cholesterol binding in the control of cholesterol by the Scap-Insig system.Eur Biophys J. 2022 Jul;51(4-5):385-399. doi: 10.1007/s00249-022-01606-z. Epub 2022 Jun 19. Eur Biophys J. 2022. PMID: 35717507 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-Protein Interactions Are a Unique Property and Defining Feature of G Protein-Coupled Receptors.Biophys J. 2020 Apr 21;118(8):1887-1900. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.03.008. Epub 2020 Mar 20. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32272057 Free PMC article.
-
Residues of TRPM8 at the Lipid-Water-Interface have Coevolved with Cholesterol Interaction and are Relevant for Diverse Health Disorders.J Membr Biol. 2024 Dec;257(5-6):345-364. doi: 10.1007/s00232-024-00319-y. Epub 2024 Aug 16. J Membr Biol. 2024. PMID: 39150496 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Cholesterol in M2 Clustering and Viral Budding Explained.J Chem Theory Comput. 2025 Jan 28;21(2):912-932. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.4c01026. Epub 2024 Nov 4. J Chem Theory Comput. 2025. PMID: 39494590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gimpl G. Interaction of G protein coupled receptors and cholesterol. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2016;199:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Simmonds A.C., East J.M., Lee A.G. Annular and non-annular binding sites on the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1982;693:398–406. - PubMed
-
- Lee A.G. How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1666:62–87. - PubMed
-
- Lee A.G. Biological membranes: the importance of molecular detail. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011;36:493–500. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

