Interfacial Binding Sites for Cholesterol on G Protein-Coupled Receptors
- PMID: 31010663
- PMCID: PMC6506644
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2019.03.025
Interfacial Binding Sites for Cholesterol on G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Abstract
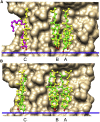
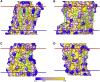
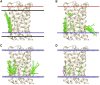
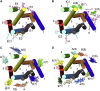
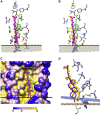
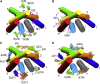
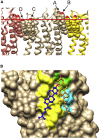
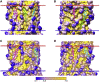
A docking procedure is described that allows the transmembrane surface of a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) to be swept rapidly for potential binding sites for cholesterol at the bilayer interfaces on the two sides of the membrane. The procedure matches 89% of the cholesterols resolved in published GPCR crystal structures, when cholesterols likely to be crystal packing artifacts are excluded. Docking poses are shown to form distinct clusters on the protein surface, the clusters corresponding to "greasy hollows" between protein ridges. Docking poses depend on the angle of tilt of the GPCR in the surrounding lipid bilayer. It is suggested that thermal motion could alter the optimal binding pose for a cholesterol molecule, with the range of binding poses within a cluster providing a guide to the range of thermal motions likely for a cholesterol within a binding site.
Copyright © 2019 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Gimpl G. Interaction of G protein coupled receptors and cholesterol. Chem. Phys. Lipids. 2016;199:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Simmonds A.C., East J.M., Lee A.G. Annular and non-annular binding sites on the (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1982;693:398–406. - PubMed
-
- Lee A.G. How lipids affect the activities of integral membrane proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2004;1666:62–87. - PubMed
-
- Lee A.G. Biological membranes: the importance of molecular detail. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011;36:493–500. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

