Biological Benefits of Ultra-high Dose Rate FLASH Radiotherapy: Sleeping Beauty Awoken
- PMID: 31010708
- PMCID: PMC6850216
- DOI: 10.1016/j.clon.2019.04.001
Biological Benefits of Ultra-high Dose Rate FLASH Radiotherapy: Sleeping Beauty Awoken
Abstract
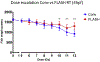
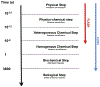
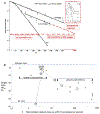
FLASH radiotherapy (FLASH-RT) is a technology that could modify the way radiotherapy is delivered in the future. This technique involves the ultra-fast delivery of radiotherapy at dose rates several orders of magnitude higher than those currently used in routine clinical practice. This very short time of exposure leads to the striking observation of relative protection of normal tissues that are exposed to FLASH-RT as compared with conventional dose rate radiotherapy. Here we summarise the current knowledge about the FLASH effect and provide a synthesis of the observations that have been reported on various experimental animal models (mice, zebrafish, pig, cats), various organs (lung, gut, brain, skin) and by various groups across 40 years of research. We also propose possible mechanisms for the FLASH effect, as well as possible paths for clinical application.
Keywords: Differential effect; FLASH radiotherapy; normal tissue protection; oxygen.
Copyright © 2019 The Royal College of Radiologists. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
FLASH Radiotherapy: The Next Technological Advance in Radiation Therapy?Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2019 Jul;31(7):405-406. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2019.05.011. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2019. PMID: 31178010 No abstract available.
References
-
- Bristow RG, Alexander B, Baumann M, Bratman SV, Brown JM, Camphausen K, et al. Combining precision radiotherapy with molecular targeting and immunomodulatory agents: a guideline by the American Society for Radiation Oncology. Lancet Oncol 2018;19(5):e240–e251. 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30096-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hornsey S, Bewley DK. Hypoxia in mouse intestine induced by electron irradiation at high dose-rates. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med 1971;19(5):479–483. - PubMed
-
- Field SB, Bewley DK. Effects of dose-rate on the radiation response of rat skin. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med 1974;26(3):259–267. - PubMed
-
- Hendry JH, Moore JV, Hodgson BW, Keene JP. The constant low oxygen concentration in all the target cells for mouse tail radionecrosis. Radiat Res 1982;92(1):172–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

