p-21 Activated Kinase as a Molecular Target for Chemoprevention in Diabetes
- PMID: 31011108
- PMCID: PMC6371191
- DOI: 10.3390/geriatrics3040073
p-21 Activated Kinase as a Molecular Target for Chemoprevention in Diabetes
Abstract
Anti-diabetic drugs modulate p-21 activated kinase (PAK) signaling. Introduction: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic inflammatory disease associated with increased cancer risk. PAK signaling is implicated in cellular homeostasis when regulated, and cancer when unrestrained. Recent reports provided a role for PAK signaling in glucose homeostasis, but the role of PAKs in the pathogenesis of T2DM is unknown. Here, we performed a mini-meta-analysis to explore if anti-diabetic drugs modify PAK signaling pathways, and provide insight regarding modulation of these pathways, to potentially reduce diabetes-associated cancer risk. Methods: PAK interacting partners in T2DM were identified using the online STRING database. Correlation studies were performed via systematic literature review to understand the effect of anti-diabetic drugs on PAK signaling. A mini-meta-analysis correlated multiple clinical studies and revealed the overall clinical response rate and percentage of adverse events in piogliazone (n = 53) and metformin (n = 91) treated patients with PAK-associated diseases. Results: A total of 30 PAK interacting partners were identified (10: reduced beta-cell mass; 10: beta-cell dysfunction; 10: obesity-insulin resistance), which were highly associated with Wnt, and G-protein signaling. The anti-diabetic drug metformin activated signaling pathways upstream; whereas pioglitazone inhibited pathways downstream of PAK. Overall, clinical response upon pioglitazone treatment was 53%. Seventy-nine percent of pioglitazone and 75% of metformin treated patients had adverse events. Pioglitazone reduced molecular-PAK biomarkers of proliferation (Ki67 and CyclinD1), and metformin had the opposite effect. Conclusions: PAK signaling in T2DM likely involves Wnt and G-protein signaling, which may be altered by the anti-diabetic drugs metformin and pioglitazone. Apart from the therapeutic limitations of adverse events, pioglitazone may be promising in chemoprevention. However long-term multi-centered studies, which initiate pioglitazone treatment early will be required to fully assess the full potential of these drugs.
Keywords: cancer; chemoprevention; inflammation; metformin; p-21 activated kinase; pioglitazone; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
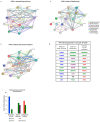
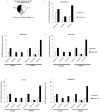


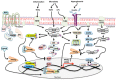
References
-
- Szklarczyk D., Franceschini A., Wyder S., Forslund K., Heller D., Huerta-Cepas J., Simonovic M., Roth A., Santos A., Tsafou K.P., et al. STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43:D447–D452. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku1003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Campregher C., Schmid G., Ferk F., Knasmuller S., Khare V., Kortum B., Dammann K., Lang M., Scharl T., Spittler A., et al. MSH3-deficiency initiates EMAST without oncogenic transformation of human colon epithelial cells. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e50541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0050541. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

