Postural Strategy in Elderly, Middle-Aged, and Young People during Local Vibratory Stimulation for Proprioceptive Inputs
- PMID: 31011128
- PMCID: PMC6371083
- DOI: 10.3390/geriatrics3040093
Postural Strategy in Elderly, Middle-Aged, and Young People during Local Vibratory Stimulation for Proprioceptive Inputs
Abstract
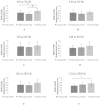
Proprioceptive input may greatly affect postural stability. However, the proprioceptive postural strategy in elderly, middle-aged, and young people has not been investigated sufficiently. Hence, in this study, we aimed to investigate differences in proprioceptive postural strategies of elderly, middle-aged, and young people. The center of pressure displacement was determined in 23 elderly, 23 middle-aged, and 23 young people during upright stance on a balance board with their eyes closed. Vibratory stimulations at 30, 60, and 240 Hz were applied to the lumbar multifidus (LM) and gastrocnemius (GS) muscles to evaluate the contributions of different proprioceptive signals used in balance control. Compared with middle-aged and young people, elderly people showed a high dependence on postural control of the GS at 30 Hz (p-values: Young and elderly: 0.033; middle-aged and elderly: 0.001). Moreover, compared with young people, elderly people were more dependent on postural control of the LM at 240 Hz (p = 0.016). There were no significant differences with respect to the GS at 60 and 240 Hz, and with respect to the LM at 30 and 60 Hz between the elderly, young, and middle-aged people. Thus, the postural control strategy of elderly people depends on the GS at 30 Hz.
Keywords: Meissner corpuscle; postural strategy; proprioceptive control.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Postural Sway in Older Patients with Sagittal Imbalance and Young Adults during Local Vibratory Proprioceptive Stimulation.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Feb 15;9(2):210. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9020210. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672014 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Back Muscle Strength and Proprioception or Mechanoreceptor Control Strategy in Postural Balance in Elderly Adults with Lumbar Spondylosis.Healthcare (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;8(1):58. doi: 10.3390/healthcare8010058. Healthcare (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164248 Free PMC article.
-
Proprioceptive Weighting Ratio for Balance Control in Static Standing Is Reduced in Elderly Patients With Non-Specific Low Back Pain.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018 Dec 15;43(24):1704-1709. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002817. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018. PMID: 30059489
-
Relationship between postural stability and fall risk in elderly people with lumbar spondylosis during local vibratory stimulation for proprioception: a retrospective study.Somatosens Mot Res. 2020 Sep;37(3):133-137. doi: 10.1080/08990220.2020.1756243. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Somatosens Mot Res. 2020. PMID: 32320628
-
Proprioceptive reliance on trunk muscles for maintaining postural stability decreases in older patients with sagittal imbalance.Gait Posture. 2023 Sep;105:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.gaitpost.2023.06.022. Epub 2023 Jul 4. Gait Posture. 2023. PMID: 37451033
Cited by
-
Differences in Proprioception Between Young and Middle-Aged Adults With and Without Chronic Low Back Pain.Front Neurol. 2020 Dec 21;11:605787. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.605787. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 33408687 Free PMC article.
-
Postural Sway in Older Patients with Sagittal Imbalance and Young Adults during Local Vibratory Proprioceptive Stimulation.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Feb 15;9(2):210. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9020210. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33672014 Free PMC article.
-
Age-related changes in leg proprioception: implications for postural control.J Neurophysiol. 2019 Aug 1;122(2):525-538. doi: 10.1152/jn.00067.2019. Epub 2019 Jun 5. J Neurophysiol. 2019. PMID: 31166819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Postural Sway during Local Vibratory Stimulation for Proprioception in Elderly Individuals with Pre-Sarcopenia.Phys Ther Res. 2020 Jul 22;23(2):149-152. doi: 10.1298/ptr.E10001. eCollection 2020. Phys Ther Res. 2020. PMID: 33489652 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Back Muscle Strength and Proprioception or Mechanoreceptor Control Strategy in Postural Balance in Elderly Adults with Lumbar Spondylosis.Healthcare (Basel). 2020 Mar 10;8(1):58. doi: 10.3390/healthcare8010058. Healthcare (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32164248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ito T., Sakai Y., Nakamura E., Yamazaki K., Yamada A., Sato N., Morita Y. Relationship between paraspinal muscle cross-sectional area and relative proprioceptive weighting ratio of older persons with lumbar spondylosis. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2015;27:2247–2251. doi: 10.1589/jpts.27.2247. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Claeys K., Brumagne S., Dankaerts W., Kiers H., Janssens L. Decreased variability in postural control strategies in young people with non-specific low back pain is associated with altered proprioceptive reweighting. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011;111:115–123. doi: 10.1007/s00421-010-1637-x. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources