A safe and potent anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy
- PMID: 31011207
- PMCID: PMC7518381
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-019-0421-7
A safe and potent anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy
Abstract
Anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies can cause severe cytokine-release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity, impeding their therapeutic application. Here we generated a new anti-CD19 CAR molecule (CD19-BBz(86)) derived from the CD19-BBz prototype bearing co-stimulatory 4-1BB and CD3ζ domains. We found that CD19-BBz(86) CAR T cells produced lower levels of cytokines, expressed higher levels of antiapoptotic molecules and proliferated more slowly than the prototype CD19-BBz CAR T cells, although they retained potent cytolytic activity. We performed a phase 1 trial of CD19-BBz(86) CAR T cell therapy in patients with B cell lymphoma (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT02842138 ). Complete remission occurred in 6 of 11 patients (54.5%) who each received a dose of 2 × 108-4 × 108 CD19-BBz(86) CAR T cells. Notably, no neurological toxicity or CRS (greater than grade 1) occurred in any of the 25 patients treated. No significant elevation in serum cytokine levels after CAR T cell infusion was detected in the patients treated, including in those who achieved complete remission. CD19-BBz(86) CAR T cells persistently proliferated and differentiated into memory cells in vivo. Thus, therapy with the new CD19-BBz(86) CAR T cells produces a potent and durable antilymphoma response without causing neurotoxicity or severe CRS, representing a safe and potent anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
X.X., Y. Liu, X.G., H.L., T.Z., P.D., J. Zhang, Y.W., S.L., M.M., X.Y., L.F., S.W. and H.S. are employees of Marino Biotechnology Corp., whose potential product was studied in this work. S.-Y.C. is a consultant of Marino Biotechnology Corp. and a recipient of a research contract with the corporation.
Figures

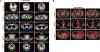


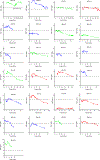


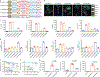
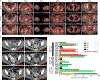

Comment in
-
Tinkering in the garage - tuning CARs for safety.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019 Sep;16(9):530-532. doi: 10.1038/s41571-019-0240-2. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31209340 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

