Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis diagnosed with radiography, CT, and bone scintigraphy
- PMID: 31011377
- PMCID: PMC6460250
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radcr.2019.03.032
Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis diagnosed with radiography, CT, and bone scintigraphy
Abstract
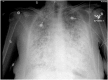
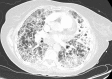
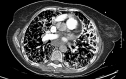
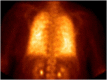
Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis is rare disease characterized by accumulation of calcium phosphate microlithis in the alveoli. The pathogenesis relates to mutation in the gene SLC34A2 (solute carrier family 34 member 2) located on chromosome 4p15.2, which produces a defective sodium-phosphate cotransporter in alveolar epithelial type-2 cells, making these cells unable to clear phosphorus released during recycling of surfactant [1].
Keywords: Alveolar microlithiasis; Bone scan scintography of the lung; Hypoxemia; Interstitial lung disease; Lung calcification; SLC34A2 gene.
Figures
References
-
- Ferreira Francisco F.A., Pereira e Silva J.L., Hochhegger B., Zanetti G., Marchiori E. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. State-of-the-art review. Respir Med. 2013;107(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Yamin, H. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis caused by two homozygous mutations, in B42. Interstitial lung disease: a potpourri of cases. p. A3438-A3438.
-
- Sahoo M.K., Karunanithi S., Bal C.S. Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: imaging characteristics of planar and SPECT/CT bone scan versus 18F-FDG and 18F-sodium fluoride PET/CT scanning. Jpn J Radiol. 2013;31(11):766–769. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

