Effect of Majun Baladur on life span, climbing ability, oxidative stress and dopaminergic neurons in the transgenic Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease
- PMID: 31011645
- PMCID: PMC6460484
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e01483
Effect of Majun Baladur on life span, climbing ability, oxidative stress and dopaminergic neurons in the transgenic Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease
Abstract
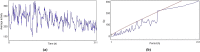
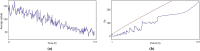
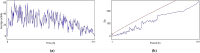
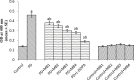
The effect of a poly herbal drug Majun Baladur (MB) was studied on the transgenic Drosophila melanogaster expressing human alpha synuclein in the neurons (PD flies). The equivalents of recommended dose for human were established for 20 g of fly food i.e. 0.0014, 0.0028, 0.0042 and 0.0056 g per 20 g of diet. The PD flies were allowed to feed on it for 24 days before performing the assays. The exposure to MB increased the life span and improves the activity of PD flies. The PD flies exposed to 0.0014, 0.0028, 0.042 and 0.0056 g of MB showed a dose dependent significant delay of 1.47, 1.88, 2.52 and 3.05 folds in the climbing ability compared to unexposed PD flies. A dose dependent significant decrease of 1.38, 1.45, 1.48 and 1.65 folds in TBARS; 1.08, 1.11, 1.17 and 1.20 folds in the GST activity; 1.20, 1.28, 1.39 and 1.52 folds in the PC content; 1.43, 1.53, 1.65 and 1.79 folds in the Caspase-9 activity; 1.21, 1.31, 1.53 and 1.64 folds in the activity of Caspase-3 and 1.24, 1.42, 1.50 and 1.79 folds in the activity of catalase; 1.50, 1.63, 1.88 and 2.06 folds in the activity of SOD in PD flies exposed to 0.0014, 0.0028, 0.042 and 0.0056 g of MB, respectively. A significant dose dependent increase of 1.20, 1.29, 1.33 and 1.44 folds in as NPSH content was observed in PD flies exposed to 0.0014, 0.0028, 0.042 and 0.0056 g of MB, respectively. The exposure to MB protects the loss of dopaminergic neurons as is evident by immunohistochemistry. It is concluded that MB is potent in reducing the PD symptoms being mimicked in the transgenic flies.
Keywords: Neuroscience.
Figures



















References
-
- Feany M.B., Bender W.W. A Drosophila model of Parkinson's disease. Nature. 2000;404:394–398. - PubMed
-
- Giasson B.I., Duda J.E., Murray I.V., Chen Q., Souza J.M., Hurtig H.I. Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective a-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science. 2000;290:985–989. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

