Improvements in CBCT Image Quality Using a Novel Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: A Clinical Evaluation
- PMID: 31011685
- PMCID: PMC6460237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.adro.2018.12.003
Improvements in CBCT Image Quality Using a Novel Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: A Clinical Evaluation
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to evaluate the clinical utility of a novel iterative cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) reconstruction algorithm for prostate and head and neck (HN) cancer.
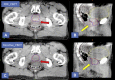
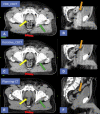
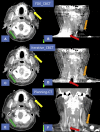
Methods and materials: A total of 10 patients with HN and 10 patients with prostate cancer were analyzed. For each patient, raw CBCT acquisition data were used to reconstruct images with a currently available algorithm (FDK_CBCT) and novel iterative algorithm (Iterative_CBCT). Quantitative contouring variation analysis was performed using structures delineated by several radiation oncologists. For prostate, observers contoured the prostate, proximal 2 cm seminal vesicles, bladder, and rectum. For HN, observers contoured the brain stem, spinal canal, right-left parotid glands, and right-left submandibular glands. Observer contours were combined to form a reference consensus contour using the simultaneous truth and performance level estimation method. All observer contours then were compared with the reference contour to calculate the Dice coefficient, Hausdorff distance, and mean contour distance (prostate contour only). Qualitative image quality analysis was performed using a 5-point scale ranging from 1 (much superior image quality for Iterative_CBCT) to 5 (much inferior image quality for Iterative_CBCT).
Results: The Iterative_CBCT data sets resulted in a prostate contour Dice coefficient improvement of approximately 2.4% (P = .029). The average prostate contour Dice coefficient for the Iterative_CBCT data sets was improved for all patients, with improvements up to approximately 10% for 1 patient. The mean contour distance results indicate an approximate 15% reduction in mean contouring error for all prostate regions. For the parotid contours, Iterative_CBCT data sets resulted in a Hausdorff distance improvement of approximately 2 mm (P < .01) and an approximate 2% improvement in Dice coefficient (P = .03). The Iterative_CBCT data sets were scored as equivalent or of better image quality for 97.3% (prostate) and 90.0% (HN) of the patient data sets.
Conclusions: Observers noted an improvement in image uniformity, noise level, and overall image quality for Iterative_CBCT data sets. In addition, expert observers displayed an improved ability to consistently delineate soft tissue structures, such as the prostate and parotid glands. Thus, the novel iterative reconstruction algorithm analyzed in this study is capable of improving the visualization for prostate and HN cancer image guided radiation therapy.
Figures
References
-
- Jaffray D.A., Siewerdsen J.H., Wong J.W., Martinez A.A. Flat-panel cone-beam computed tomography for image-guided radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;53:1337–1349. - PubMed
-
- White E., Brock K., Jaffray D., Catton C. Inter-observer variability of prostate delineation on cone beam computerised tomography images. Clin Oncol. 2009;21:32–38. - PubMed
-
- Sonke J.J., Rossi M., Wolthaus J., van Herk M., Damen E., Belderbos J. Frameless stereotactic body radiotherapy for lung cancer using four-dimensional cone beam CT guidance. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2009;74:567–574. - PubMed
-
- Purdie T.G., Bissonnette J.P., Franks K. Cone-beam computed tomography for on-line image guidance of lung stereotactic radiotherapy: Localization, verification, and intrafraction tumor position. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007;68:243–252. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

