A Region-Based Deep Level Set Formulation for Vertebral Bone Segmentation of Osteoporotic Fractures
- PMID: 31011954
- PMCID: PMC7064662
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-019-00216-0
A Region-Based Deep Level Set Formulation for Vertebral Bone Segmentation of Osteoporotic Fractures
Abstract
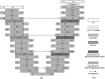
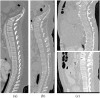
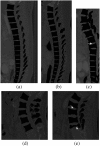
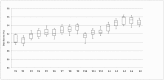
Accurate segmentation of the vertebrae from medical images plays an important role in computer-aided diagnoses (CADs). It provides an initial and early diagnosis of various vertebral abnormalities to doctors and radiologists. Vertebrae segmentation is very important but difficult task in medical imaging due to low-contrast imaging and noise. It becomes more challenging when dealing with fractured (osteoporotic) cases. This work is dedicated to address the challenging problem of vertebra segmentation. In the past, various segmentation techniques of vertebrae have been proposed. Recently, deep learning techniques have been introduced in biomedical image processing for segmentation and characterization of several abnormalities. These techniques are becoming popular for segmentation purposes due to their robustness and accuracy. In this paper, we present a novel combination of traditional region-based level set with deep learning framework in order to predict shape of vertebral bones accurately; thus, it would be able to handle the fractured cases efficiently. We termed this novel Framework as "FU-Net" which is a powerful and practical framework to handle fractured vertebrae segmentation efficiently. The proposed method was successfully evaluated on two different challenging datasets: (1) 20 CT scans, 15 healthy cases, and 5 fractured cases provided at spine segmentation challenge CSI 2014; (2) 25 CT image data (both healthy and fractured cases) provided at spine segmentation challenge CSI 2016 or xVertSeg.v1 challenge. We have achieved promising results on our proposed technique especially on fractured cases. Dice score was found to be 96.4 ± 0.8% without fractured cases and 92.8 ± 1.9% with fractured cases in CSI 2014 dataset (lumber and thoracic). Similarly, dice score was 95.2 ± 1.9% on 15 CT dataset (with given ground truths) and 95.4 ± 2.1% on total 25 CT dataset for CSI 2016 datasets (with 10 annotated CT datasets). The proposed technique outperformed other state-of-the-art techniques and handled the fractured cases for the first time efficiently.
Keywords: Computer-aided diagnosis; Deep learning; Medical image analysis; Vertebrae segmentation; Vertebral osteoporotic fracture.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Automatic vertebrae localization and segmentation in CT with a two-stage Dense-U-Net.Sci Rep. 2021 Nov 12;11(1):22156. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-01296-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34772972 Free PMC article.
-
Spine X-ray image segmentation based on deep learning and marker controlled watershed.J Xray Sci Technol. 2025 Jan;33(1):109-119. doi: 10.1177/08953996241299998. Epub 2024 Dec 19. J Xray Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 39973775
-
Iterative fully convolutional neural networks for automatic vertebra segmentation and identification.Med Image Anal. 2019 Apr;53:142-155. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2019.02.005. Epub 2019 Feb 12. Med Image Anal. 2019. PMID: 30771712
-
Automatic Segmentation of Multiple Organs on 3D CT Images by Using Deep Learning Approaches.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1213:135-147. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-33128-3_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32030668 Review.
-
Deep learning-based automatic segmentation of images in cardiac radiography: A promising challenge.Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022 Jun;220:106821. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2022.106821. Epub 2022 Apr 19. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2022. PMID: 35487181 Review.
Cited by
-
A Classification Method for Thoracolumbar Vertebral Fractures due to Basketball Sports Injury Based on Deep Learning.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Oct 5;2022:8747487. doi: 10.1155/2022/8747487. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. PMID: 36245837 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Segmentation for Favourable Delineation of Ten Wrist Bones on Wrist Radiographs Using Convolutional Neural Network.J Pers Med. 2022 May 11;12(5):776. doi: 10.3390/jpm12050776. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35629198 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Age Assessment Empowered with Deep Learning: A Survey, Open Research Challenges and Future Directions.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Oct 3;10(10):781. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10100781. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33022947 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fast Segmentation of Vertebrae CT Image Based on the SNIC Algorithm.Tomography. 2022 Jan 3;8(1):59-76. doi: 10.3390/tomography8010006. Tomography. 2022. PMID: 35076637 Free PMC article.
-
Deep Learning-Based Medical Images Segmentation of Musculoskeletal Anatomical Structures: A Survey of Bottlenecks and Strategies.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jan 19;10(2):137. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10020137. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829631 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Levangie PK, Norkin CC: Joint structure and function: a comprehensive analysis, 5th edition. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Co, p. 140 Print 2011
-
- Middleditch A, Olive J. 2nd. Oxford: MCSP. Butterworth-Heinemann; 2005. Functional anatomy of the spine.
-
- Wang KC, Jeanmenne A, Weber GM, Thawait S, Carrino JA. An online evidence-based decision support system for distinguishing benign from malignant vertebral compression fractures by magnetic resonance imaging feature analysis. J Digit Imaging. 2010;24(3):507–515. doi: 10.1007/s10278-010-9316-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

