Estrogen receptor α promotes Cav1.2 ubiquitination and degradation in neuronal cells and in APP/PS1 mice
- PMID: 31012223
- PMCID: PMC6612642
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12961
Estrogen receptor α promotes Cav1.2 ubiquitination and degradation in neuronal cells and in APP/PS1 mice
Abstract
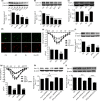
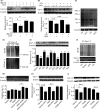
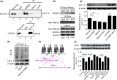
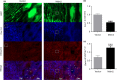
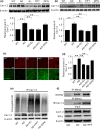
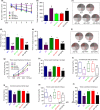
Cav1.2 is the pore-forming subunit of L-type voltage-gated calcium channel (LTCC) that plays an important role in calcium overload and cell death in Alzheimer's disease. LTCC activity can be regulated by estrogen, a sex steroid hormone that is neuroprotective. Here, we investigated the potential mechanisms in estrogen-mediated regulation of Cav1.2 protein. We found that in cultured primary neurons, 17β-estradiol (E2) reduced Cav1.2 protein through estrogen receptor α (ERα). This effect was offset by a proteasomal inhibitor MG132, indicating that ubiquitin-proteasome system was involved. Consistently, the ubiquitin (UB) mutant at lysine 29 (K29R) or the K29-deubiquitinating enzyme TRAF-binding protein domain (TRABID) attenuated the effect of ERα on Cav1.2. We further identified that the E3 ligase Mdm2 (double minute 2 protein) and the PEST sequence in Cav1.2 protein played a role, as Mdm2 overexpression and the membrane-permeable PEST peptides prevented ERα-mediated Cav1.2 reduction, and Mdm2 overexpression led to the reduced Cav1.2 protein and the increased colocalization of Cav1.2 with ubiquitin in cortical neurons in vivo. In ovariectomized (OVX) APP/PS1 mice, administration of ERα agonist PPT reduced cerebral Cav1.2 protein, increased Cav1.2 ubiquitination, and improved cognitive performances. Taken together, ERα-induced Cav1.2 degradation involved K29-linked UB chains and the E3 ligase Mdm2, which might play a role in cognitive improvement in OVX APP/PS1 mice.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Cav1.2; Estrogen receptor α; K29; Mdm2; ubiquitination.
© 2019 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of an estrogen receptor α non covalent ubiquitin-binding surface: role in 17β-estradiol-induced transcriptional activity.J Cell Sci. 2013 Jun 15;126(Pt 12):2577-82. doi: 10.1242/jcs.123307. Epub 2013 Apr 16. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23591816
-
Regulation and the Mechanism of Estrogen on Cav1.2 Gene in Rat-Cultured Cortical Astrocytes.J Mol Neurosci. 2016 Oct;60(2):205-13. doi: 10.1007/s12031-016-0803-y. Epub 2016 Aug 6. J Mol Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27498200
-
The autocrine motility factor receptor delays the pathological progression of Alzheimer's disease via regulating the ubiquitination-mediated degradation of APP.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Apr 29;17(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01741-7. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40301979 Free PMC article.
-
The ubiquitin E3 ligase Parkin regulates neuronal CaV1.3 channel functional expression.J Neurophysiol. 2022 Dec 1;128(6):1555-1564. doi: 10.1152/jn.00287.2022. Epub 2022 Nov 9. J Neurophysiol. 2022. PMID: 36350063
-
Impaired autophagy and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of Beclin 1 interactome.Prog Neurobiol. 2013 Jul-Aug;106-107:33-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2013.06.002. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Prog Neurobiol. 2013. PMID: 23827971 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein modification in neurodegenerative diseases.MedComm (2020). 2024 Aug 4;5(8):e674. doi: 10.1002/mco2.674. eCollection 2024 Aug. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39105197 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BAG2-Mediated Inhibition of CHIP Expression and Overexpression of MDM2 Contribute to the Initiation of Endometriosis by Modulating Estrogen Receptor Status.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Apr 27;8:554190. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.554190. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33987175 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the non-classical estrogen pathway in neurodegenerative diseases and brain injury disorders.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Sep 15;13:999236. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.999236. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36187099 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caldendrin represses neurite regeneration and growth in dorsal root ganglion neurons.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 14;13(1):2608. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29622-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36788334 Free PMC article.
-
ELK1 inhibition alleviates amyloid pathology and memory decline by promoting the SYVN1-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of PS1 in Alzheimer's disease.Exp Mol Med. 2025 May;57(5):1032-1046. doi: 10.1038/s12276-025-01455-8. Epub 2025 May 1. Exp Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40307574 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altier, C. , Garcia‐Caballero, A. , Simms, B. , You, H. , Chen, L. , Walcher, J. , … Zamponi, G. W. (2011). The Cavbeta subunit prevents RFP2‐mediated ubiquitination and proteasomal degradation of L‐type channels. Nature Neuroscience, 14, 173–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

