Activation of the calcium sensing receptor attenuates TRPV6-dependent intestinal calcium absorption
- PMID: 31013259
- PMCID: PMC6629117
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.128013
Activation of the calcium sensing receptor attenuates TRPV6-dependent intestinal calcium absorption
Abstract
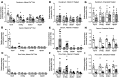
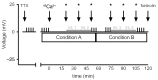
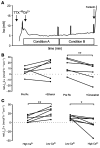
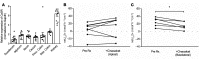
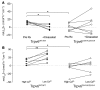
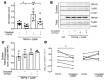
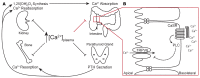
Plasma calcium (Ca2+) is maintained by amending the release of parathyroid hormone and through direct effects of the Ca2+ sensing receptor (CaSR) in the renal tubule. Combined, these mechanisms alter intestinal Ca2+ absorption by modulating 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3 production, bone resorption, and renal Ca2+ excretion. The CaSR is a therapeutic target in the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism and hypocalcemia a common complication of calcimimetic therapy. The CaSR is also expressed in intestinal epithelium, however, a direct role in regulating local intestinal Ca2+ absorption is unknown. Chronic CaSR activation decreased expression of genes involved in Ca2+ absorption. In Ussing chambers, increasing extracellular Ca2+ or basolateral application of the calcimimetic cinacalcet decreased net Ca2+ absorption across intestinal preparations acutely. Conversely, Ca2+ absorption increased with decreasing extracellular Ca2+ concentration. These responses were absent in mice expressing a non-functional TRPV6, TRPV6D541A. Cinacalcet also attenuated Ca2+ fluxes through TRPV6 in Xenopus oocytes when co-expressed with the CaSR. Moreover, the phospholipase C inhibitor, U73122, prevented cinacalcet-mediated inhibition of Ca2+ flux. These results reveal a regulatory pathway whereby activation of the CaSR in the basolateral membrane of the intestine directly attenuates local Ca2+ absorption via TRPV6 to prevent hypercalcemia and help explain how calcimimetics induce hypocalcemia.
Keywords: Calcium; Calcium channels; Gastroenterology; Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Toka HR, Pollak MR, Houillier P. Calcium sensing in the renal tubule. Physiology (Bethesda) 2015;30(4):317–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

