Identification of key regulatory genes connected to NF-κB family of proteins in visceral adipose tissues using gene expression and weighted protein interaction network
- PMID: 31013288
- PMCID: PMC6478283
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0214337
Identification of key regulatory genes connected to NF-κB family of proteins in visceral adipose tissues using gene expression and weighted protein interaction network
Abstract
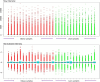
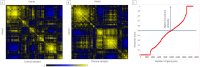
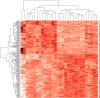
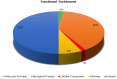
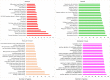
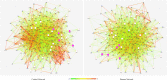
Obesity is connected to the activation of chronic inflammatory pathways in both adipocytes and macrophages located in adipose tissues. The nuclear factor (NF)-κB is a central molecule involved in inflammatory pathways linked to the pathology of different complex metabolic disorders. Investigating the gene expression data in the adipose tissue would potentially unravel disease relevant gene interactions. The present study is aimed at creating a signature molecular network and at prioritizing the potential biomarkers interacting with NF-κB family of proteins in obesity using system biology approaches. The dataset GSE88837 associated with obesity was downloaded from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO) database. Statistical analysis represented the differential expression of a total of 2650 genes in adipose tissues (p = <0.05). Using concepts like correlation, semantic similarity, and theoretical graph parameters we narrowed down genes to a network of 23 genes strongly connected with NF-κB family with higher significance. Functional enrichment analysis revealed 21 of 23 target genes of NF-κB were found to have a critical role in the pathophysiology of obesity. Interestingly, GEM and PPP1R13L were predicted as novel genes which may act as potential target or biomarkers of obesity as they occur with other 21 target genes with known obesity relationship. Our study concludes that NF-κB and prioritized target genes regulate the inflammation in adipose tissues through several molecular signaling pathways like NF-κB, PI3K-Akt, glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, angiogenesis and cytokine pathways. This integrated system biology approaches can be applied for elucidating functional protein interaction networks of NF-κB protein family in different complex diseases. Our integrative and network-based approach for finding therapeutic targets in genomic data could accelerate the identification of novel drug targets for obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dissecting the Role of NF-κb Protein Family and Its Regulators in Rheumatoid Arthritis Using Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network.Front Genet. 2019 Nov 20;10:1163. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.01163. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31824568 Free PMC article.
-
Lucidone Promotes the Cutaneous Wound Healing Process via Activation of the PI3K/AKT, Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017 Jan;1864(1):151-168. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.10.021. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 27816443
-
Construction of Parkinson's disease marker-based weighted protein-protein interaction network for prioritization of co-expressed genes.Gene. 2019 May 20;697:67-77. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.026. Epub 2019 Feb 16. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30776463
-
Antagonistic crosstalk between NF-κB and SIRT1 in the regulation of inflammation and metabolic disorders.Cell Signal. 2013 Oct;25(10):1939-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.06.007. Epub 2013 Jun 11. Cell Signal. 2013. PMID: 23770291 Review.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative proteomic network analyses support depot-specific roles for leucine rich repeat LGI family member 3 in adipose tissues.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Aug;22(2):837. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10269. Epub 2021 Jun 4. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34149883 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of key host gene-microbe networks in the cecum tissues of the obese rabbits induced by a high-fat diet.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jun 14;14:1407051. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1407051. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38947127 Free PMC article.
-
SMAD1 as a biomarker and potential therapeutic target in drug-resistant multiple myeloma.Biomark Res. 2021 Jun 16;9(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s40364-021-00296-7. Biomark Res. 2021. PMID: 34134766 Free PMC article.
-
The Extra-Virgin Olive Oil Polyphenols Oleocanthal and Oleacein Counteract Inflammation-Related Gene and miRNA Expression in Adipocytes by Attenuating NF-κB Activation.Nutrients. 2019 Nov 21;11(12):2855. doi: 10.3390/nu11122855. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31766503 Free PMC article.
-
CHCHD4-TRIAP1 regulation of innate immune signaling mediates skeletal muscle adaptation to exercise.Cell Rep. 2024 Jan 23;43(1):113626. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113626. Epub 2023 Dec 28. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38157298 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

