Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Tauopathy
- PMID: 31013607
- PMCID: PMC6514575
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20081959
Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and Tauopathy
Abstract
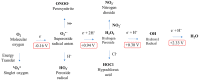
Tauopathy is a collective term for neurodegenerative diseases associated with pathological modifications of tau protein. Tau modifications are mediated by many factors. Recently, reactive oxygen species (ROS) have attracted attention due to their upstream and downstream effects on tauopathy. In physiological conditions, healthy cells generate a moderate level of ROS for self-defense against foreign invaders. Imbalances between ROS and the anti-oxidation pathway cause an accumulation of excessive ROS. There is clear evidence that ROS directly promotes tau modifications in tauopathy. ROS is also highly upregulated in the patients' brain of tauopathies, and anti-oxidants are currently prescribed as potential therapeutic agents for tauopathy. Thus, there is a clear connection between oxidative stress (OS) and tauopathies that needs to be studied in more detail. In this review, we will describe the chemical nature of ROS and their roles in tauopathy.
Keywords: oxidative stress; reactive oxygen species; tauopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Shin R.W., Iwaki T., Kitamoto T., Tateishi J. Hydrated autoclave pretreatment enhances tau immunoreactivity in formalin-fixed normal and Alzheimer’s disease brain tissues. Lab. Investig. 1991;64:693–702. - PubMed
-
- Miyata Y., Hoshi M., Nishida E., Minami Y., Sakai H. Binding of microtubule-associated protein 2 and tau to the intermediate filament reassembled from neurofilament 70-kDa subunit protein. Its regulation by calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1986;261:13026–13030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

