Radioprotective Effect of Walnut Oligopeptides Against Gamma Radiation-Induced Splenocyte Apoptosis and Intestinal Injury in Mice
- PMID: 31013611
- PMCID: PMC6515242
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24081582
Radioprotective Effect of Walnut Oligopeptides Against Gamma Radiation-Induced Splenocyte Apoptosis and Intestinal Injury in Mice
Abstract
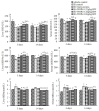
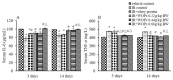
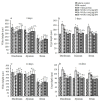
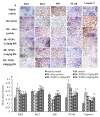
Walnut oligopeptides (WOPs) intake is associated with the augment of the antioxidant defense system and immune system. The chief object of this study is to evaluate the radioprotective effect of walnut oligopeptides extracted from walnut seed protein against 60Coγ-irradiation induced damage in mice. Female BALB/c mice were administered WOPs through drinking water for 14 days until a single dose of whole-body 60Coγ-irradiation. The 30-day survival test was carried out in the first group (8 Gy), and the other two groups (3.5 Gy) were sacrificed at 3 days and 14 days post-irradiation. Blood and organ samples of mice in the three groups were collected, the histopathological analysis and immunohistochemistry were conducted. The number of peripheral blood leukocytes, bone marrow DNA content, inflammatory cytokines, antioxidant capacity, and intestinal permeability were measured. We found that the administration of WOPs augmented antioxidant defense system, accelerated hematopoietic recovery and showed the significant trend toward higher survival rate and less weight loss compared with non-administrated control mice. In addition, WOPs administration appeared to be important to limit IR-induced splenocyte apoptosis and inflammatory cascade as well as reduce intestine epithelial barrier dysfunction and promote epithelial integrity. These results suggest that pre and post-treatment of WOPs may help to ameliorate acute damage, which is induced by ionizing radiation in mice and accelerate its recovery.
Keywords: antioxidant; epithelial barrier; immunosuppression; splenocyte apoptosis; walnut oligopeptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Small Molecule Oligopeptides Isolated from Walnut (Juglans regia L.) and Their Anti-Fatigue Effects in Mice.Molecules. 2018 Dec 22;24(1):45. doi: 10.3390/molecules24010045. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30583565 Free PMC article.
-
The Gastroprotective Effect of Small Molecule Oligopeptides Isolated from Walnut (Juglans regia L.) against Ethanol-Induced Gastric Mucosal Injury in Rats.Nutrients. 2020 Apr 18;12(4):1138. doi: 10.3390/nu12041138. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32325708 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of TNF-α and free radicals reduces systematic inflammatory and metabolic disorders: Radioprotective effects of ginseng oligopeptides on intestinal barrier function and antioxidant defense.J Nutr Biochem. 2017 Feb;40:53-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.09.019. Epub 2016 Oct 26. J Nutr Biochem. 2017. PMID: 27863345
-
Radioprotective Effect of Whey Hydrolysate Peptides against γ-Radiation-Induced Oxidative Stress in BALB/c Mice.Nutrients. 2021 Mar 2;13(3):816. doi: 10.3390/nu13030816. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33801268 Free PMC article.
-
Review of the evidence of radioprotective potential of creatine and arginine as dietary supplements.Int J Radiat Biol. 2024;100(6):849-864. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2024.2345098. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Int J Radiat Biol. 2024. PMID: 38683545 Review.
Cited by
-
Ferulic Acid Protects Human Lens Epithelial Cells against Ionizing Radiation-Induced Oxidative Damage by Activating Nrf2/HO-1 Signal Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 May 10;2022:6932188. doi: 10.1155/2022/6932188. eCollection 2022. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022. PMID: 35592532 Free PMC article.
-
Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Oligopeptides Alleviate Alcohol-Induced Acute Liver Injury through the Inhibition of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Rats.Nutrients. 2023 May 6;15(9):2210. doi: 10.3390/nu15092210. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432394 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effects of ferulic acid against ionizing radiation-induced oxidative damage in rat lens through activating Nrf2 signal pathway.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 May 18;16(5):687-693. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.05.03. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37206165 Free PMC article.
-
EGCG's anticancer potential unveiled: triggering apoptosis in lung cancer cell lines through in vitro investigation.PeerJ. 2025 Mar 26;13:e19135. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19135. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40161336 Free PMC article.
-
Protective rules of natural antioxidants against gamma-induced damage-A review.Food Sci Nutr. 2021 Jul 21;9(9):5263-5278. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.2469. eCollection 2021 Sep. Food Sci Nutr. 2021. PMID: 34532033 Free PMC article.
References
-
- He L.X., Wang J.B., Sun B., Zhao J., Li L., Xu T., Li H., Sun J.Q., Ren J., Liu R., et al. Suppression of TNF-alpha and free radicals reduces systematic inflammatory and metabolic disorders: Radioprotective effects of ginseng oligopeptides on intestinal barrier function and antioxidant defense. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017;40:53–61. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2016.09.019. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

