mACPpred: A Support Vector Machine-Based Meta-Predictor for Identification of Anticancer Peptides
- PMID: 31013619
- PMCID: PMC6514805
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20081964
mACPpred: A Support Vector Machine-Based Meta-Predictor for Identification of Anticancer Peptides
Abstract
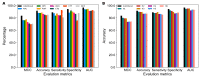
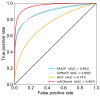
Anticancer peptides (ACPs) are promising therapeutic agents for targeting and killing cancer cells. The accurate prediction of ACPs from given peptide sequences remains as an open problem in the field of immunoinformatics. Recently, machine learning algorithms have emerged as a promising tool for helping experimental scientists predict ACPs. However, the performance of existing methods still needs to be improved. In this study, we present a novel approach for the accurate prediction of ACPs, which involves the following two steps: (i) We applied a two-step feature selection protocol on seven feature encodings that cover various aspects of sequence information (composition-based, physicochemical properties and profiles) and obtained their corresponding optimal feature-based models. The resultant predicted probabilities of ACPs were further utilized as feature vectors. (ii) The predicted probability feature vectors were in turn used as an input to support vector machine to develop the final prediction model called mACPpred. Cross-validation analysis showed that the proposed predictor performs significantly better than individual feature encodings. Furthermore, mACPpred significantly outperformed the existing methods compared in this study when objectively evaluated on an independent dataset.
Keywords: anticancer peptides; feature selection; optimal features; sequential forward search; support vector machine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
mACPpred 2.0: Stacked Deep Learning for Anticancer Peptide Prediction with Integrated Spatial and Probabilistic Feature Representations.J Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 1;436(17):168687. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2024.168687. Epub 2024 Jun 25. J Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39237191
-
ACPred: A Computational Tool for the Prediction and Analysis of Anticancer Peptides.Molecules. 2019 May 22;24(10):1973. doi: 10.3390/molecules24101973. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31121946 Free PMC article.
-
ACPred-FL: a sequence-based predictor using effective feature representation to improve the prediction of anti-cancer peptides.Bioinformatics. 2018 Dec 1;34(23):4007-4016. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty451. Bioinformatics. 2018. PMID: 29868903 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of Machine Learning Algorithms in the Prediction and Design of Anticancer Peptides.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(12):1242-1250. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666200117171403. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 31957610 Review.
-
Large-scale comparative review and assessment of computational methods for anti-cancer peptide identification.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Jul 20;22(4):bbaa312. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbaa312. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33316035 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LGBM-ACp: an ensemble model for anticancer peptide prediction and in silico screening with potential drug targets.Mol Divers. 2024 Aug;28(4):1965-1981. doi: 10.1007/s11030-023-10602-0. Epub 2023 Jan 13. Mol Divers. 2024. PMID: 36637711
-
To Assist Oncologists: An Efficient Machine Learning-Based Approach for Anti-Cancer Peptides Classification.Sensors (Basel). 2022 May 25;22(11):4005. doi: 10.3390/s22114005. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35684624 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Peptides Inducing Cancer Cell Death: Mechanisms and Properties of Specific Candidates for Cancer Therapeutics.Molecules. 2021 Dec 9;26(24):7453. doi: 10.3390/molecules26247453. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34946535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Peptides: An Update on Classifications and Databases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 28;22(21):11691. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111691. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New Bioactive Peptides from the Mediterranean Seagrass Posidonia oceanica (L.) Delile and Their Impact on Antimicrobial Activity and Apoptosis of Human Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 15;24(6):5650. doi: 10.3390/ijms24065650. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36982723 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

