Evaluation of Polyphenolic Compounds and Pharmacological Activities in Hairy Root Cultures of Ligularia fischeri Turcz. f. spiciformis (Nakai)
- PMID: 31013652
- PMCID: PMC6515212
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24081586
Evaluation of Polyphenolic Compounds and Pharmacological Activities in Hairy Root Cultures of Ligularia fischeri Turcz. f. spiciformis (Nakai)
Abstract
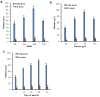
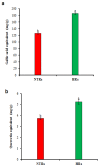
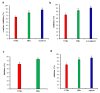
A considerable amount of bioactive compounds have been used for the biopharmaceutical engineering to help human health and nutrition. Hairy root culture (HRC) or transgenic root is a favourable alternative technique for phytochemical production. Ligularia fischeri is a significant source of pharmaceutically important active compounds with an enormous range of health care applications. HRC of L. fischeri was developed using Agrobacterium rhizogenes for the production of polyphenolic compounds with antioxidant, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, anticancer and anti-inflammatory pharmaceutical activities. Hairy roots (HRs) were selected by morphological assessment, genetic and molecular analyses. The maximum accumulation of fresh mass (94.15 g/L) and dry mass (9.45 g/L) was recorded in MS liquid medium supplemented with 30 g/L sucrose at 28 days. Furthermore, HRs successfully produced numerous polyphenolic compounds, including six hydroxycinnamic acids, seven flavonols, seven hydroxybenzoic acids, vanillin, resveratrol, pyrogallol, homogentisic, and veratric acids, which were identified by UHPLC analysis. HRs produced higher total phenolic (185.65 mg/g), and flavonoid (5.25 mg/g) contents than non-transformed roots (125.55 mg/g and 3.75 mg/g). As a result of these metabolic changes, pharmaceutical activities were found higher in HRs than non-transformed roots (NTRs). The present study indicates that HRC has the potential to increase the content of beneficial polyphenolic compounds with higher potential pharmaceutical activities. To the best of our knowledge, the present study is the first report on enhancing the production of polyphenolic compounds with pharmaceutical activities from the HRCs of L. fischeri.
Keywords: Agrobacterium rhizogenes; Ligularia fischeri; hairy root cultures; pharmaceutical activities; polyphenolic compounds.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Li J.P., Wang C.F., Liu T., Zhang Y.B., Liu Y.Z., Zhang Z.Z. Chemical constituents from the roots of Ligularia fischeri Turcz. Nat. Prod. Res. Dev. 2011;23:1014–1016.
-
- Hong S., Joo T., Jhoo J.W. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of 3,5-dicaffeoylquinic acid isolated from Ligularia fischeri leaves. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015;24:257–263. doi: 10.1007/s10068-015-0034-y. - DOI
-
- Granato D., Shahidi F., Wrolstad R., Kilmartin P., Melton L.D., Hidalgo F.J., Miyashita K., van Camp J., Alasalvar C., Ismail A.B., et al. Antioxidant activity, total phenolics and flavonoids contents: should we ban in vitro screening methods? Food Chem. 2018;264:471–475. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

